Soft fibromas (papillomas)
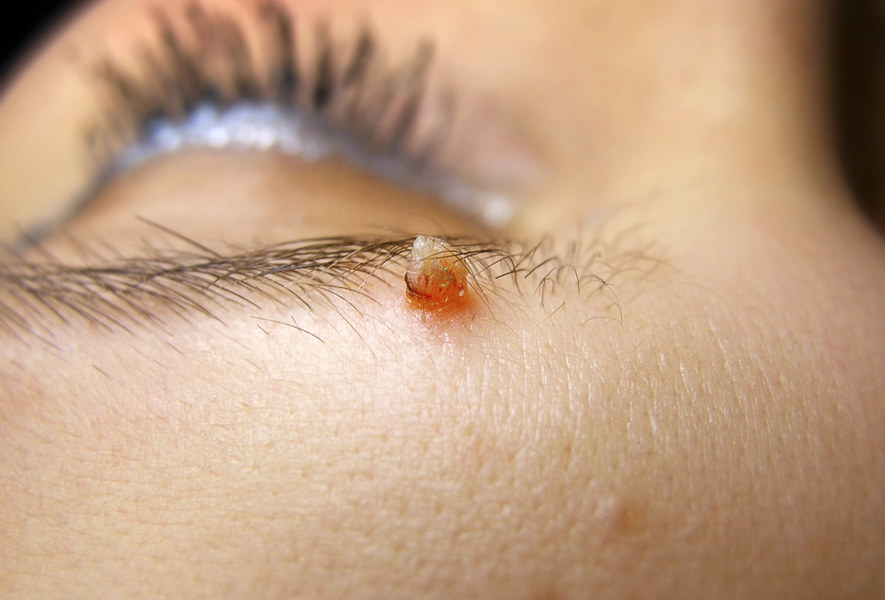
Soft fibroids (papillomas) are benign, non-infectious, non-contagious skin lesions that are harmless to health. However, if they are continuously traumatised, the conditions for infection are created.
Clinical signs
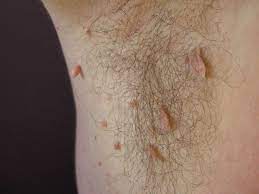
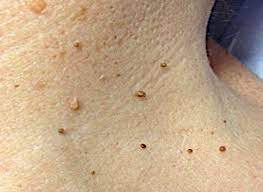
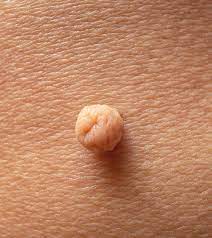
- a skin-coloured or brownish small bump on a thin leg
- typical sites: neck, armpits, pubic area, groin in women, less commonly eyelids
- may be multiple
- painless
Risk factors
- genetic predisposition
- overweight, obesity
- high blood cholesterol
- glucose intolerance, diabetes mellitus
- due to hormonal changes in the body during pregnancy
- there is no consensus on whether the HPV virus is involved in the development of soft fibroids
- based on clinical features (discussed above)
- by examining the lesion with a dermatoscope (a special device that magnifies structures) according to the characteristic dermatoscopic features.
Treatment
- Removal of soft fibroids is recommended if they are persistently traumatised, obstructive, bleeding, or if they interfere with vision in the eyelid area. However, they are usually removed for aesthetic reasons.
- treatment methods are destructive: small ones can be removed by cryotherapy (cold treatment in a medical facility using carbon dioxide or liquid nitrogen), larger ones by electrosurgery or laser treatment
- soft fibroids that appear during pregnancy may disappear on their own a few months after birth
There is no definite explanation for soft fibroids, so the only way to prevent them is to adjust risk factors: maintain a normal body weight (BMI under 25), and adjust blood cholesterol levels if needed.
IMPORTANT:
There is a common misconception that all skin lesions on the foot are papillomas. Neurofibromas (a genetic disease manifested in the skin), papillomatous moles, especially if they have deeper pigmentation and are visible as skin-coloured nodules on the body, and infectious molluscs or thread warts, can also sometimes support papillomas at first glance. Therefore, we do not recommend self-treatment of soft fibroids (papillomas) at home.

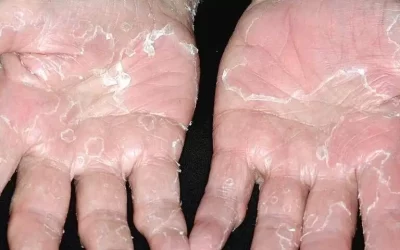
Peeling skin syndrome
Peeling skin syndrome is a genetic disorder characterized by constant peeling of the skin. The disease appears from birth or in the first year of life
lasts a lifetime
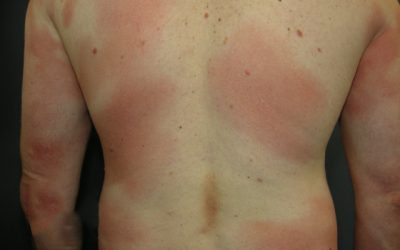
Mycosis Fungoides
The most common primary skin T-cell lymphoma (cancer of the blood). Mycosis Fungoides is characterized by three main stages, several of which may exist at the same time
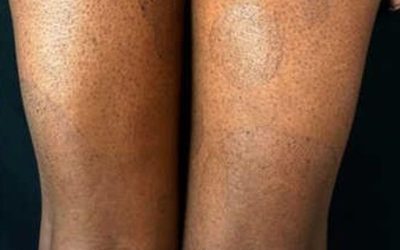
Paraneoplastic dermatological manifestation of gastrointestinal malignancies
rare disorders resulting from the immune system’s response to a cancerous process (neoplasia) in the body. Gastrointestinal neoplasms more often cause paraneoplastic syndromes affecting the skin.
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškės g. 99, Vilnius
+370 671 33323
info@iderma.lt