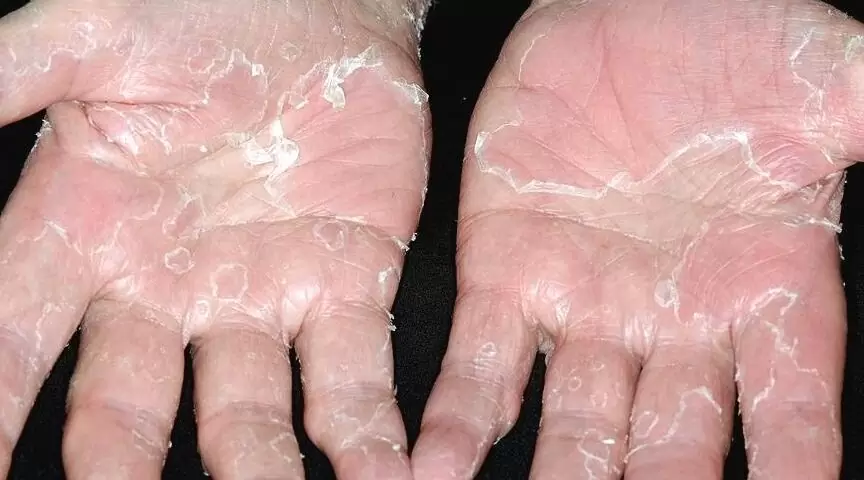
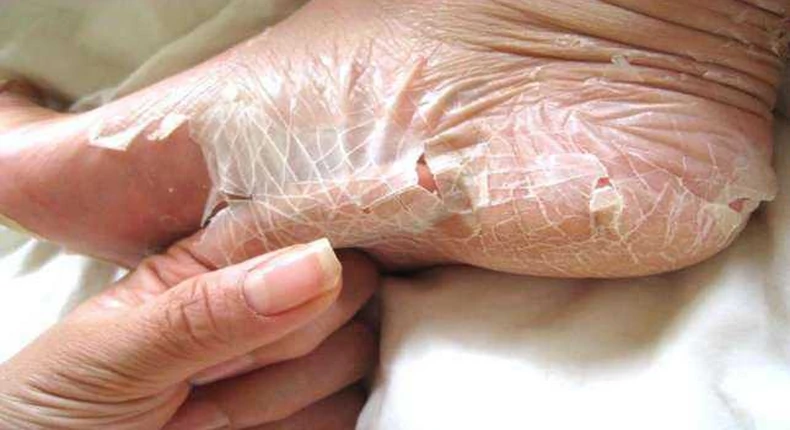
Peeling skin syndrome
- the disease appears from birth or in the first year of life
- lasts a lifetime
- a very rare disease that, according to available data, affects men and women equally
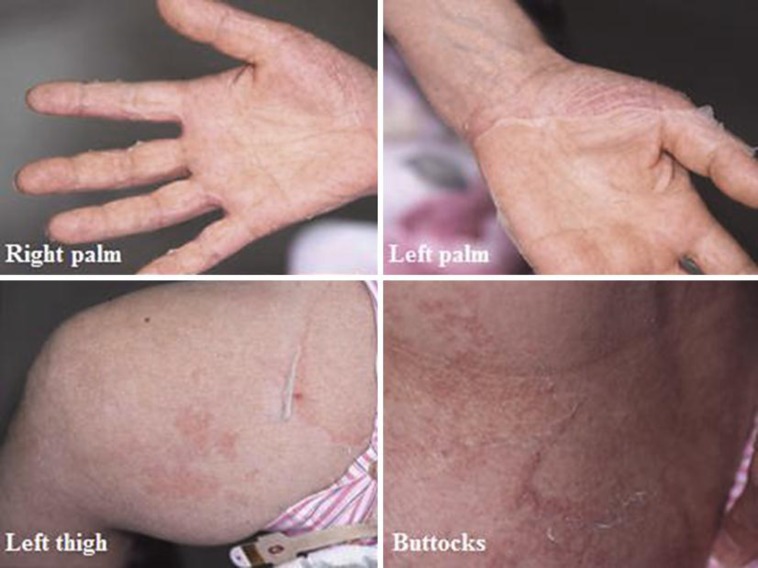
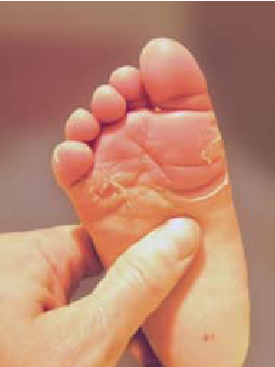
It occurs most often:
- constant skin peeling, flaking
- there is no soreness or unpleasant sensations when peeling the skin
- the skin is dry
- the skin may become scaly, reminiscent of fish skin
- peeling can be triggered by sunburn, sweat, mechanical damage, etc
Localization
possible skin changes on the whole body or only on the extremities
- in the case of a widespread form in the newborn, other immune system and metabolic disorders often appear together, which often results in the patients not surviving
- in the case of a localized form, the lesions can be of very different degrees, so some affected individuals remain undiagnosed
other related changes:
- short height
- disturbed puberty
Diagnostics
Patient survey and examination data are very important for diagnosis. However, a skin biopsy is required to confirm the diagnosis, and blood and urine tests can also help.
Treatment
The Dermatologist tailors a personalized care approach for each individual. This includes broad strategies like safeguarding the skin from harm or irritation.
The treatment may involve a range of hydrating lotions, topical applications that aid in skin renewal, oral medications to support skin health, and occasionally, treatments to manage allergic reactions.

Vitiligo – Why Do White Patches Appear on the Skin and How to Treat Them?
Vitiligo is a non-contagious skin condition characterized by white patches due to the loss of pigment. While it does not pose a direct threat to physical health, it can have a significant psychological impact. Learn what causes vitiligo, its symptoms, how it is diagnosed, and which treatment methods are currently available.
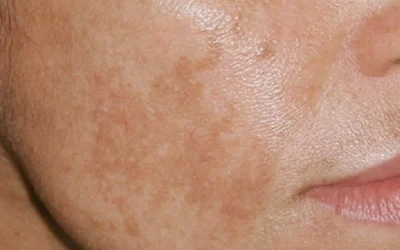
Hyperpigmentation: Causes, Types, and Modern Treatment Options
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by dark spots that appear due to sun exposure, hormonal changes, or skin damage. In this article, you will learn about the main types and causes of hyperpigmentation, as well as how to effectively treat it using modern dermatological methods and preventive care.
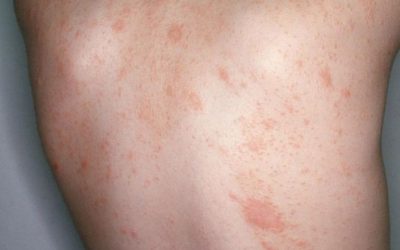
Pityriasis rosea
An acute, self-limiting, exanthematic skin disease that manifests as itchy, somewhat inflammatory, scaly rashes, usually on the torso, chest, and upper limbs.