Pitted Keratolysis
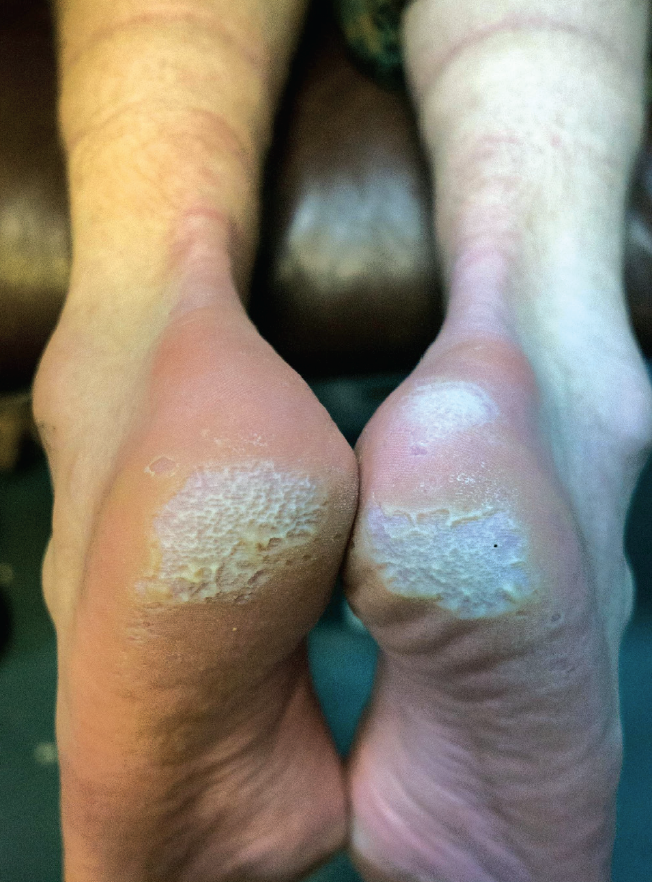
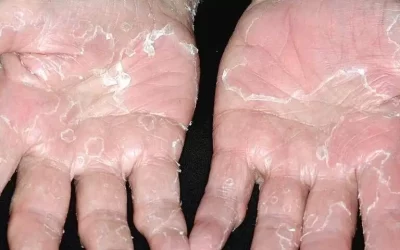
Pitted Keratolysis – non-inflammatory, bacterial skin disease of the palms and soles. Punctate pits are visible in the damaged skin, and an unpleasant smell is felt.
Risk factors:
- profuse sweating
- closed, air-tight footwear
- increased skin pH
- obesity
- diabetes
- immunosuppressive conditions
In the presence of these risk factors and the contribution of bacteria (Corynebacteria, Kytococcus sedentarius, Derma*****lus congolensis, Actinomyces, etc.), enzymes released by them destroy the stratum corneum of the skin and form a characteristic point lesion resembling small pits, “craters”. Sulfur-containing substances are released during this process, which causes a strong unpleasant smell.
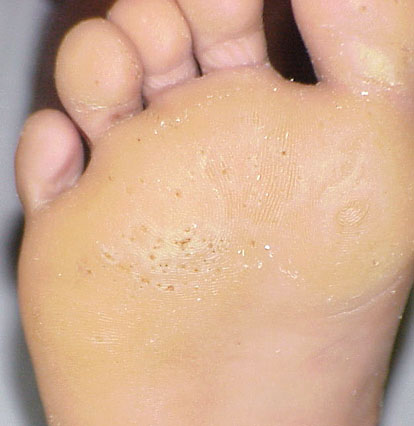
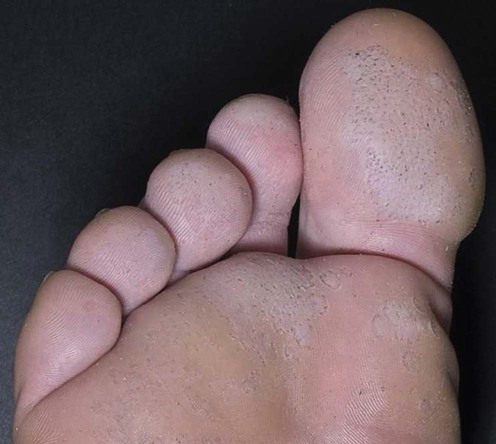
Unpleasant smell of damaged areas, as if pitted, usually the surface of the skin of the soles (palms are extremely rarely affected). Lesions can coalesce, forming hollow furrows. The rash mostly occurs in the places that rest on the surface when walking – the areas of the toes and the heel. It may itch and hurt.
Diagnostics
Diagnosed by the characteristic clinical picture. In the case of a very widespread, confluent rash, Wood’s lamp examination, microscopic examination, or skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment:
an antibacterial wash and locally used antibacterial drugs are prescribed, selected according to the spread of the disease. Injections may be given to reduce sweating of the palms and soles.
Prevention:
- wear non-pressing, “breathable” footwear
- change shoe insoles regularly
- avoid sharing footwear with others
- wear natural fiber socks
- in case of damage to the soles, wash the socks at a temperature of 60° C to remove bacteria
- keep the feet clean
- reduce excessive sweating (antiperspirants, injections)

Peeling skin syndrome
Peeling skin syndrome is a genetic disorder characterized by constant peeling of the skin. The disease appears from birth or in the first year of life
lasts a lifetime
Mycosis Fungoides
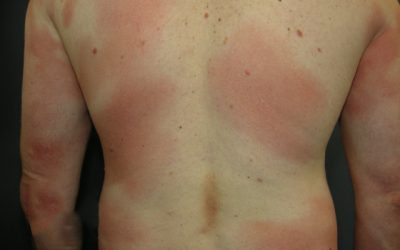
The most common primary skin T-cell lymphoma (cancer of the blood). Mycosis Fungoides is characterized by three main stages, several of which may exist at the same time
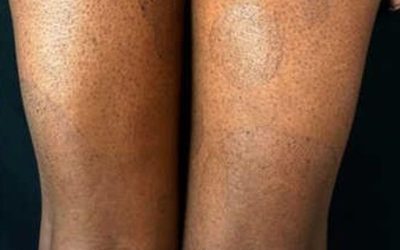
Paraneoplastic dermatological manifestation of gastrointestinal malignancies
rare disorders resulting from the immune system’s response to a cancerous process (neoplasia) in the body. Gastrointestinal neoplasms more often cause paraneoplastic syndromes affecting the skin.
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškių g. 99, Vilnius
+370 670 70822
info@iderma.lt