Geographic tongue

- Characteristic of 1-3% of the population in the world
- Children are rarely affected, and women are twice as often affected as men
- The exact cause of the disease remains unknown, but it has been observed that it occurs significantly more often in patients who suffer from psoriasis or various allergic and immune system diseases
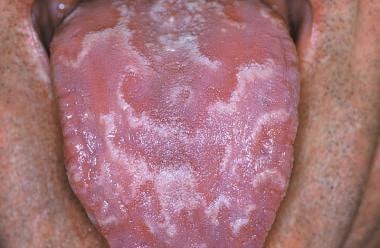
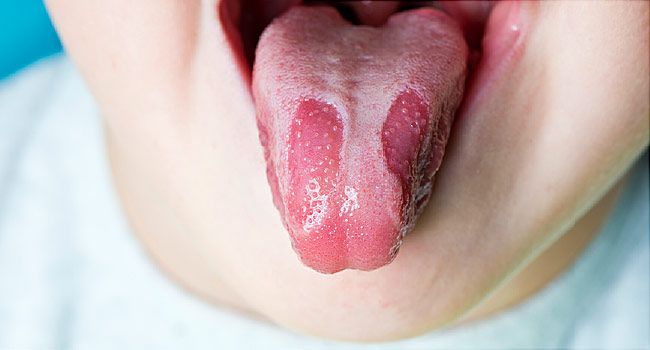
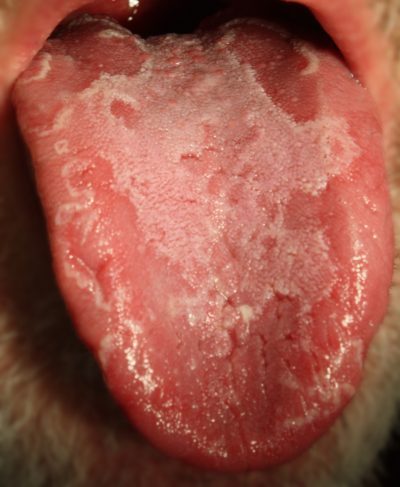
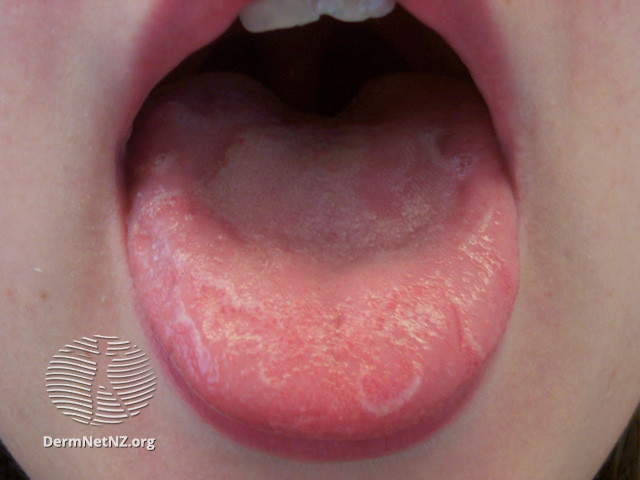
Geographic tongue is characterized by:
- irregularly shaped, red, map-like, smooth or swollen spots surrounded by white lines
- can appear suddenly, persist for months or even longer, and later recur
There are often no other obvious symptoms, except that in some cases there may be burning or irritation sensations, especially when eating spicy, hot or sour foods.
Data from the patient’s interview and examination are usually sufficient to establish the diagnosis. If additional laboratory tests are performed, their results are usually normal.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for geographic tongue. The main measure to reduce the feeling of discomfort is to avoid hot, spicy, acidic food. During the consultation, the doctor can personally draw up a general treatment plan aimed at reducing specific symptoms that are bothering the patient.
The following can be used for this:
- local anesthetics
- topically applied hormones or other drugs
- antihistamine or anesthetic mouthwashes

Skin conditions in newborns
It is in the early period of the newborn that various adaptive changes in the skin of the newborn are observed, manifested as it adapts to new environmental conditions.
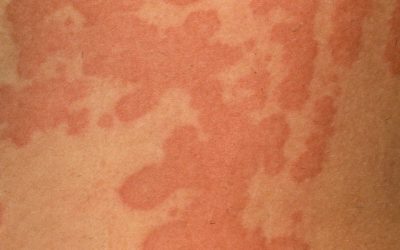
Acute urticaria
an acute vascular skin reaction that manifests as swelling of the skin, raised red blisters that are very itchy.
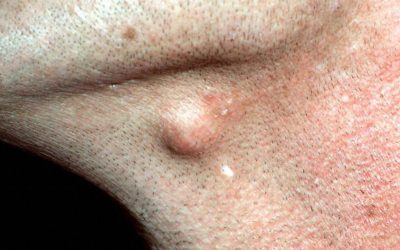
Epidermoid cysts
Benign skin formation (cyst) formed at the place of hair growth, inside is usually filled with keratin and fatty filler.