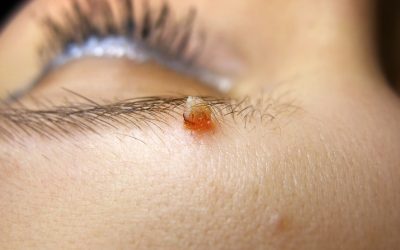
Furuncle
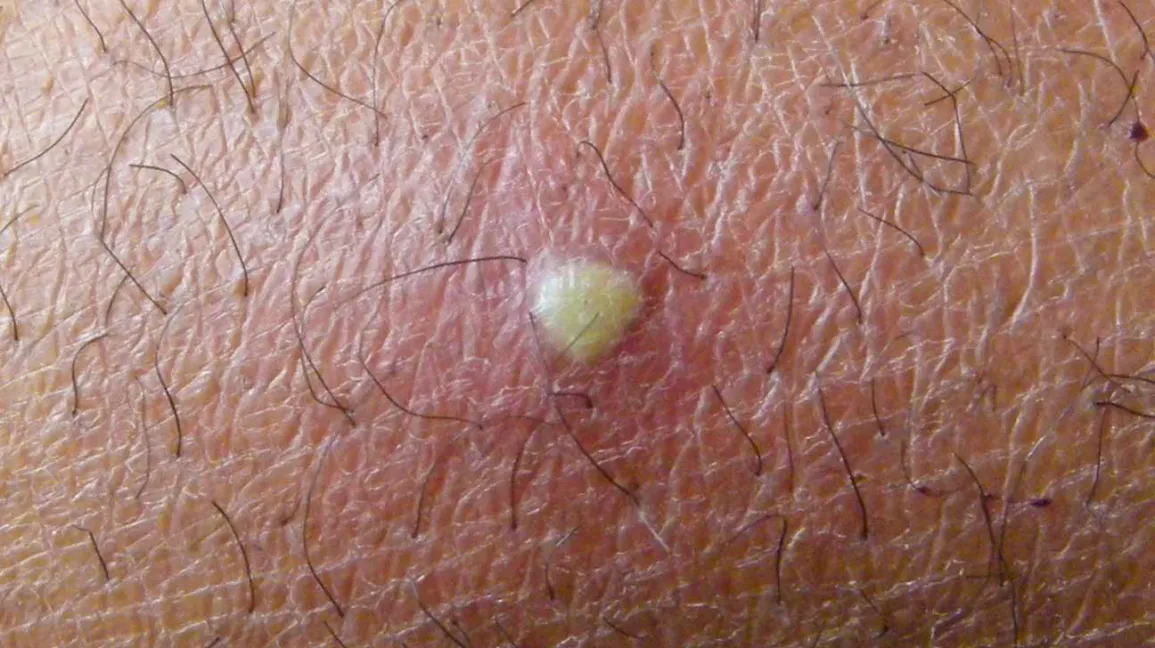
- The most common causative agent is S. aureus (up to 75%)
- About 10-20% of people carry these bacteria on their skin
- Furuncle is common in healthy people who take care of their hygiene
Risk factors
Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing a boil:
- Constant presence (carrying) of infectious bacteria in the nostrils, around the anus, in body folds
- Diabetes
- Obesity, older age
- Weakening of the immune system (severe illnesses, chemotherapy, other drugs affecting the immune system)
- Foreign bodies in the skin (sutures, catheters, piercings)
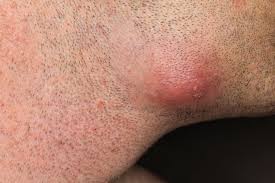
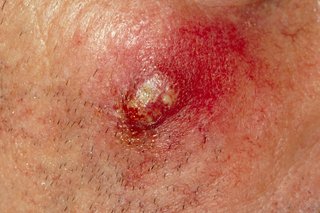
Furuncle is characterized by:
- A painful, red, tender, palpable nodule or pustule (abscess) that collects purulent secretions
- The size can vary from the size of a small pustule to 5 centimeters
- When the secretion accumulates, it usually ruptures and pus flows out
- A hair follicle (black dot) may be visible in the center of the nodule/pustule
- Swelling of the surrounding skin is possible
Localization
face, neck, armpits, thighs and buttocks. Especially the places where the hair grows the most, the skin sweats the most and is otherwise traumatized
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of furuncle is usually determined based on the patient’s survey and examination data. In rarer cases, when the collected data is insufficient or it is desired to find out the exact causative agent, additional tests are available to clarify the diagnosis:
- Microscopic examination (stained infectious agents are examined under a microscope), Microbiological studies (a colony of the bacteria that caused the infection is grown in a special medium)
- General blood test (there may be signs of infection: increase in leukocytes, neutrophils)
- CRB study (moderate increase possible)
Treatment and prognosis
During the consultation, the doctor determines the most appropriate treatment method for each patient. Common treatment approaches include:
- In cases where the furuncle is large, does not rupture naturally, or the purulent discharge persists, a general surgical approach may be necessary to remove the pus.
- Application of antiseptics to the affected area.
- Antibiotic therapy may be considered based on the extent of the infection. The choice of antibiotics is generally guided by test results.
Lesions typically heal within a few weeks, although scarring can occur. Preventative measures include eliminating risk factors, maintaining personal hygiene, and boosting immunity.

Soft fibromas (papillomas)
Soft fibromas (papillomas) Soft fibroids (papillomas) are benign, non-infectious, non-contagious skin lesions that are harmless...
Multi-coloured ringworm
Multi-coloured ringworm Multi-coloured ringworm is a skin rash caused by a fungus of the Malassezia species, called...
Dishidrotic eczema
Dishidrotic eczema Dishidrotic eczema (syn. dishidrotic dermatitis, dishidrotic dermatitis, pompholyx) is a chronic,...