Atopinis dermatitas mažam vaikui
Atopinis dermatitas (ang. atopic dermatitis) – lėtinė uždegiminė odos liga, kuri dažniausiai pirmą kartą pasireiškia 3 – 6 mėnesių amžiaus vaikams.
- Pasaulyje atopiniu dermatitu serga 5-20% vaikų
- Didžiajai daliai sergančiųjų simptomai išnyksta iki pilnametystės, nors gali vėliau atsinaujinti
- Liga būdinga vaikams, sergantiems kitomis alerginėmis ligomis
- Atopinio dermatito pasireiškimui didelę įtaką daro paveldimumas
Rizikos veiksniai
Atopinio dermatito pasireiškimą gali išprovokuoti tam tikri veiksniai:
- Įvairūs alergenai: maisto, aplinkos (namų dulkės, dulkių erkutės, žiedadulkės ir kiti), kontaktiniai alergenai (nikelis, chromas ir kiti)
- Odos išsausėjimas
- Odos infekcijos
- Dirgikliai (vilna, sintetika, skalbimo milteliai, statybinės medžiagos ir kiti)
- Netinkamas klimatas, dažnas prakaitavimas
- Psichologinis stresas
Klinika
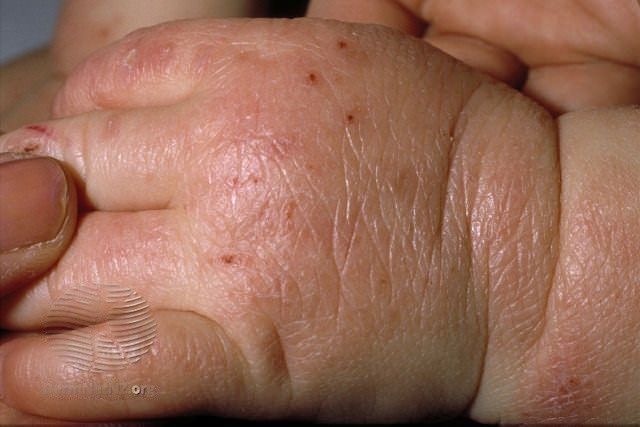
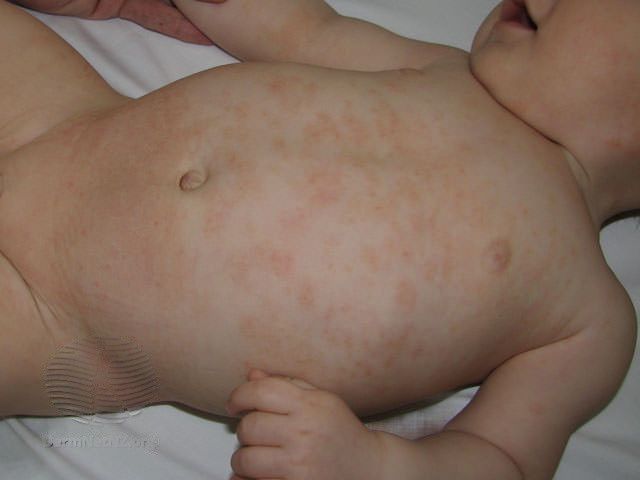
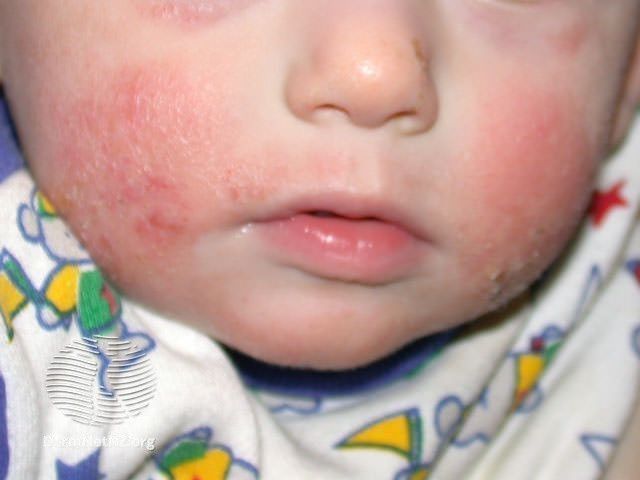
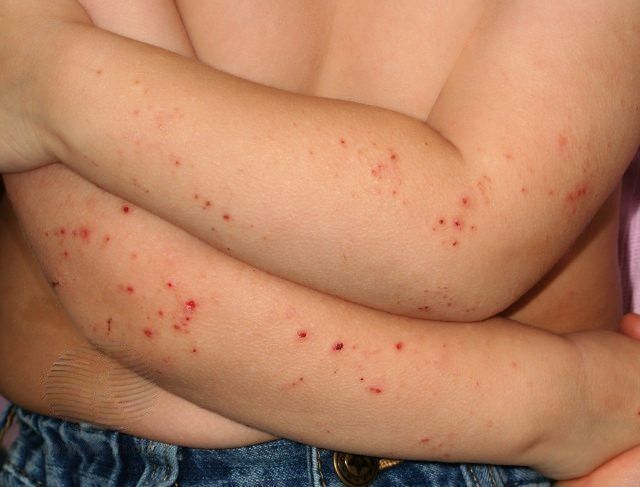
Atopinis dermatitas kūdikiams ir mažiems vaikams (iki 4 metų) pasireiškia šiek tiek kitaip nei suaugusiems asmenims:
- būdingi riboto ploto įvairaus dydžio paraudę apčiuopiami odos iškilimai, pūslelės
- vyrauja odos paraudimas, šlapiavimas, šašai
- būdingas stiprus niežėjimas
- gali prisidėti miego, nuotaikos problemos
- lokalizacija: veidas, kaklas, krūtinė, galvos plaukuotoji dalis, tiesiamieji (išoriniai), o rečiau lenkiamieji (vidiniai) galūnių paviršiai
Diagnostika
Diagnozei nustatyti dažniausiai pakanka paciento apklausos ir apžiūros duomenų. Atopinis dermatitas dažnai būdingas vaikams, sergantiems alerginėmis ligomis, todėl gali būti atliekami papildomi tyrimai:
- Kraujo tyrimas IgE koncentracijai nustatyti
- Odos alerginiai mėginiai
- Odos biopsija (retais atvejais, diagnozei patvirtinti)
Gydymas
Konsultacijos metu gydymas kiekvienam pacientui parenkamas asmeniškai, atsižvelgiant į paciento bendrą būklę, amžių, ligos sunkumą. Gydymui gali būti naudojami:
- Drėkinamieji kremai, emolientai
- Hormonų (gliukokortikoidų) ir kiti tepalai
- Antihistamininiai vaistai
- Antibiotikų tepalai ar geriamieji vaistai (prasidėjus antrinei bakterinei odos infekcijai)
- Fototerapija
- Imuninę sistemą keičiantys vaistai
Taip pat svarbu ir kitos bendrosios priemonės:
- Nukirpti vaiko nagus trumpai, kad būtų išvengta nukasymų ir iš to sekančios antrinės bakterinės odos infekcijos
- Naudoti specialias jautriai odai skirtas higienos priemones
- Vengti dirgiklių, alergenų


Žymės
Vitiligo – Why Do White Patches Appear on the Skin and How to Treat Them?
Vitiligo is a non-contagious skin condition characterized by white patches due to the loss of pigment. While it does not pose a direct threat to physical health, it can have a significant psychological impact. Learn what causes vitiligo, its symptoms, how it is diagnosed, and which treatment methods are currently available.
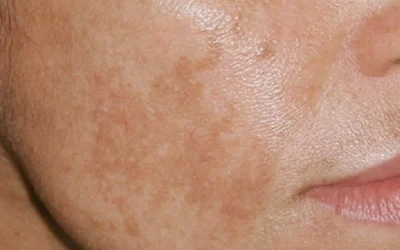
Hyperpigmentation: Causes, Types, and Modern Treatment Options
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by dark spots that appear due to sun exposure, hormonal changes, or skin damage. In this article, you will learn about the main types and causes of hyperpigmentation, as well as how to effectively treat it using modern dermatological methods and preventive care.
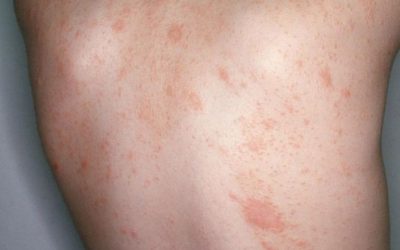
Pityriasis rosea
An acute, self-limiting, exanthematic skin disease that manifests as itchy, somewhat inflammatory, scaly rashes, usually on the torso, chest, and upper limbs.
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškių g. 99, Vilnius
+370 670 70822
info@iderma.lt



Recent Comments