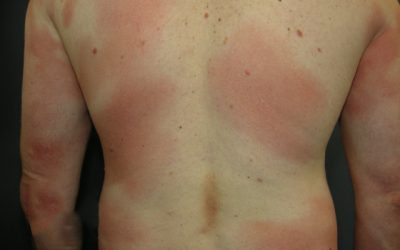
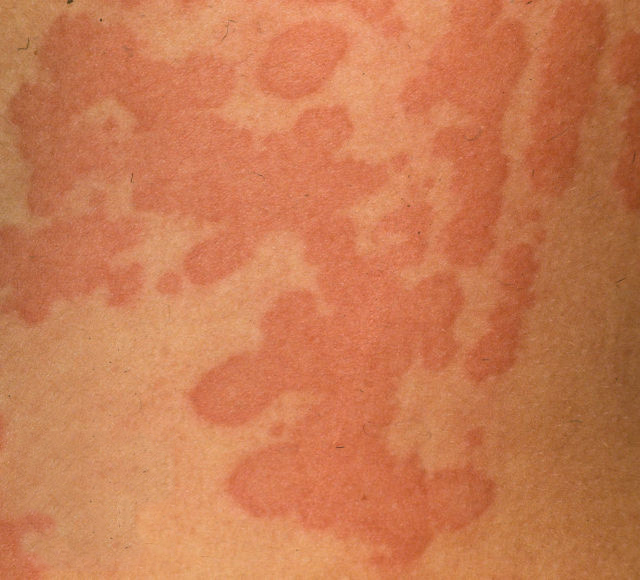
Acute urticaria
- Most often, urticaria occurs as a separate reaction of the body
- In rare cases, the onset of an anaphylactic reaction may occur
- One in five adults or children will experience at least one episode of urticaria in their lifetime
- Characteristic for people with other allergic diseases (atopic dermatitis, bronchial asthma and others)
- The causes of urticaria in most cases (30-50%) remain unknown
- Other less common causes: infectious diseases, medications, certain foods
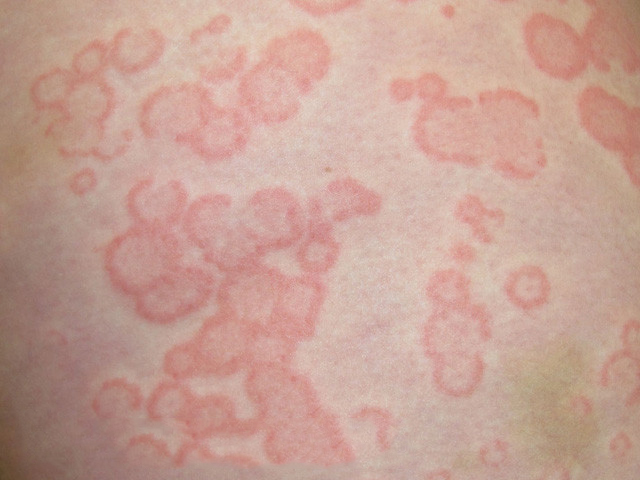
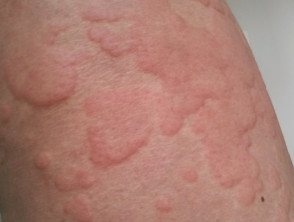
Acute urticaria is characterized by:
- rash:
- pustules – a raised, red, itchy rash of different sizes and shapes that goes away within 24 hours.
- angioedema – a sudden appearance of a red or skin-colored, strongly raised rash, swelling of the deeper layers of the skin, as well as more often characterized by burning, pressing, pain rather than itching; can last up to 72 hours
- localization: can affect any part of the body
- starts spontaneously
- repeated no longer than 6 weeks
The patient’s survey and examination data are usually sufficient to establish the diagnosis. In addition, provocation samples may be performed. If the symptoms are repeated and in order to find out the cause of the urticaria, a thorough examination is needed.
Treatment
During the consultation, the treatment is selected for each patient individually.
Can be used for treatment
- second generation antihistamine (antiallergic) drugs
- oral hormones
Medicines are used until the symptoms disappear.
Prognosis
Urticaria rash usually goes away on its own without leaving any marks on the skin, but it tends to recur. If urticaria recurs for more than 6 weeks, then it is classified as chronic urticaria.

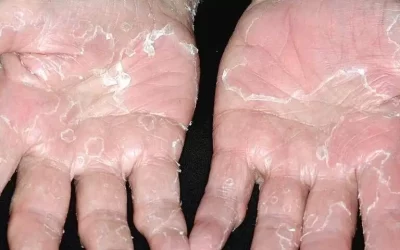
Peeling skin syndrome
Peeling skin syndrome is a genetic disorder characterized by constant peeling of the skin. The disease appears from birth or in the first year of life
lasts a lifetime
Mycosis Fungoides
The most common primary skin T-cell lymphoma (cancer of the blood). Mycosis Fungoides is characterized by three main stages, several of which may exist at the same time
Paraneoplastic dermatological manifestation of gastrointestinal malignancies
rare disorders resulting from the immune system’s response to a cancerous process (neoplasia) in the body. Gastrointestinal neoplasms more often cause paraneoplastic syndromes affecting the skin.
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškių g. 99, Vilnius
+370 670 70822
info@iderma.lt