Peeling skin syndrome
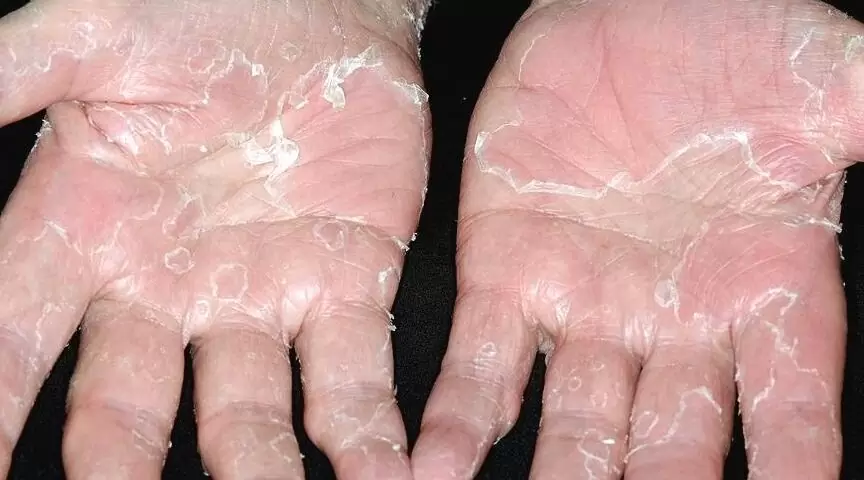
- the disease appears from birth or in the first year of life
- lasts a lifetime
- a very rare disease that, according to available data, affects men and women equally
It occurs most often:
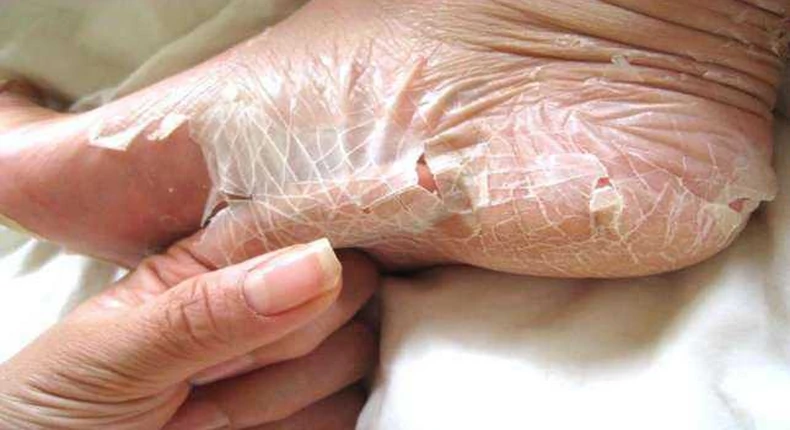
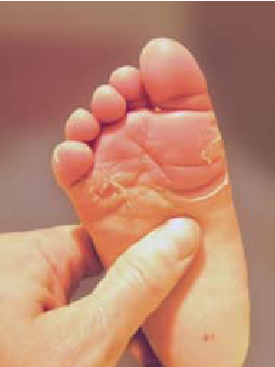
- constant skin peeling, flaking
- there is no soreness or unpleasant sensations when peeling the skin
- the skin is dry
- the skin may become scaly, reminiscent of fish skin
- peeling can be triggered by sunburn, sweat, mechanical damage, etc
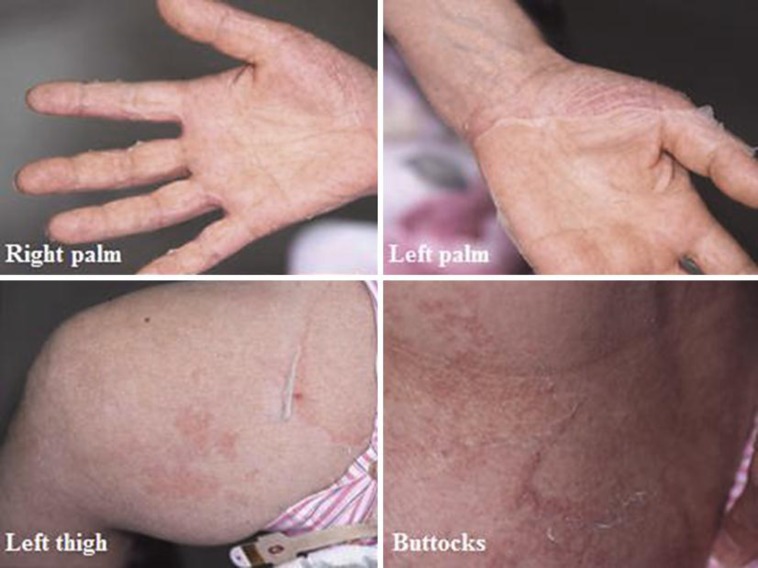
Localization
possible skin changes on the whole body or only on the extremities
- in the case of a widespread form in the newborn, other immune system and metabolic disorders often appear together, which often results in the patients not surviving
- in the case of a localized form, the lesions can be of very different degrees, so some affected individuals remain undiagnosed
other related changes:
- short height
- disturbed puberty
Diagnostics
Patient survey and examination data are very important for diagnosis. However, a skin biopsy is required to confirm the diagnosis, and blood and urine tests can also help.
Treatment
The Dermatologist tailors a personalized care approach for each individual. This includes broad strategies like safeguarding the skin from harm or irritation.
The treatment may involve a range of hydrating lotions, topical applications that aid in skin renewal, oral medications to support skin health, and occasionally, treatments to manage allergic reactions.

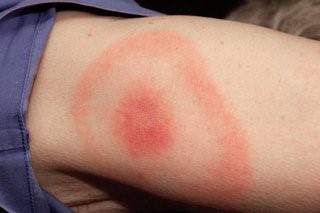
Lyme disease
It is contracted when a blood-sucking tick injects intestinal contents containing bacteria into a wound. Untreated Lyme disease can damage not only the skin, but also the internal organs, joints and nervous system.
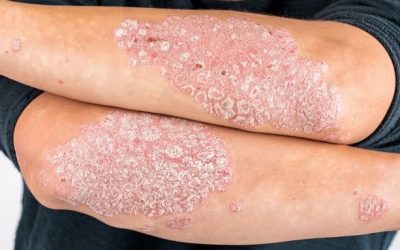
Psoriasis
A common, chronic, inflammatory, recurring skin disease that affects 2-3% of the population. Psoriasis can start at any age, and is most often found in adults.
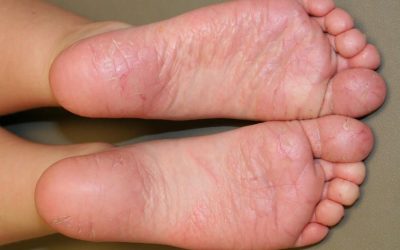
Juvenile plantar dermatosis
a disease characterized by localized damage to the feet. JPD usually occurs in children between the ages of 3 and 14 who are prone to atopy or have atopic dermatitis