Flat lichen
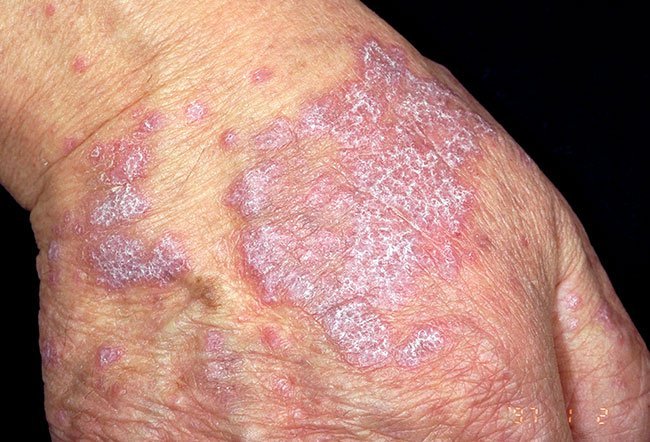
Lupus plan us/ruber: An inflammatory disease of the skin and/or mucous membranes of unknown origin, characterised by characteristic papules (palpable bumps on the skin) that resemble lichen (lichen planus). The disease can also damage hair follicles and nail plates.
Prevalence and causes of the disease:
- affects 0.25-1% of the EU population. population
- Most cases occur between 30 and 60 years of age.
- Children are less likely to be ill
- men and women get sick with the same frequency
- The cause of the disease remains unclear. It is usually an unexplained reaction to an unknown stimulus/factor.
Risk factors
- Stress
- Viral diseases (hepatitis B, C infections)
- Autoimmune processes (primary biliary cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease)
- Certain medicines (blood pressure regulators, antimalarials, anticonvulsants…)
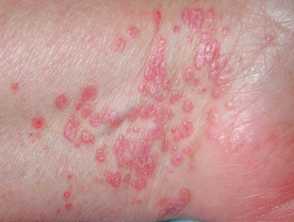
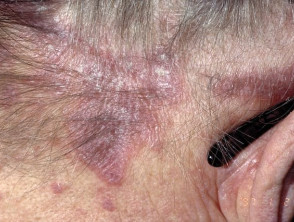
The 6 P rule is used to describe the main symptoms:
- Planar – flat
- Polygonal – polygonal
- Pruritic – itchy
- Purple – purple
- Papule – papules (palpable bumps on the skin)
- Plaques (larger than papules, palpable bumps on the skin)
Localisation:
- Wrists, forearms, ankles, shins, sacrum, trunk
- Mucosal
- Nails, hair
The Kiobner phenomenon is characterised by the appearance of new rash elements on healthy skin in areas affected by external irritation.
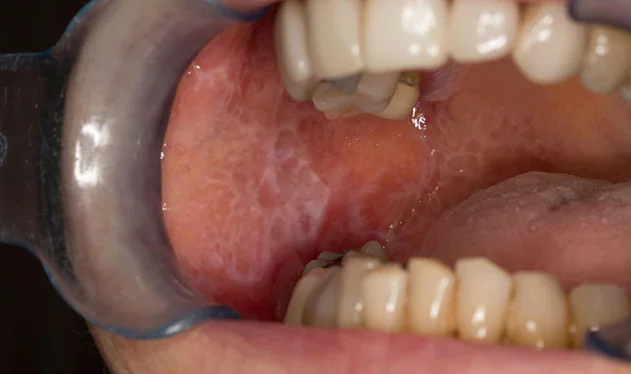
Mucosal lesions (25-75%):
- In Burna, 40-60% of the total. cases of Wickham’s reticulum (a wide whitish reticulum on the cheeks, tongue or gums)
- Papules, plaques and painful erosions (defects in the superficial mucous layer) also appear in the mucous membranes
Lesions in the genital organs occur in 20% of cases. cases (penis and scrotum in men, labia and vagina in women):
- whitish reticulation, papules, annular rashes, erosions (defects in the superficial layer of the skin)
- narrowing of the foreskin in men (phimosis, strictures)
- if left untreated, squamous cell carcinoma develops
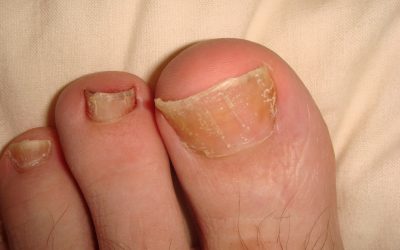
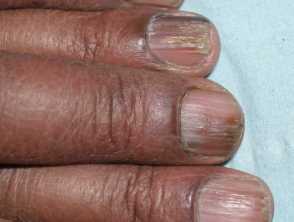
Nail damage – 16%.
- longitudinal fractures on the nail (Latin: pterygium)
- nail plate damage, decay (onychodystrophy, onychoatrophy)
Hair loss (alopecia) on the hairy part of the head
Diagnostics
For a diagnosis, it is usually enough to:
- medical history (family history is important in 10% of cases; medications used are important)
- clinics
Less commonly, if history and clinical data are insufficient, it may be necessary to:
- skin or mucosal biopsies (for histological confirmation)
- screening for comorbidities:
-
- markers of infection
- cancerous processes
- gastrointestinal diseases
-
Treatment and prognosis
During the consultation, the treatment is selected for each patient individually. Depending on the spread and severity of the disease, topical agents, systemic drugs and light therapy (phototherapy) may be used.
Prognosis – Spontaneous resolution of symptoms in 2/3 of cases within 1 year.
50%. skin lesions heal within 9 months.
Recommendations
If you notice any of the above symptoms, you should contact your family doctor or a dermatovenerologist directly. During the consultation, a specific treatment will be prescribed, which must be followed precisely.
Certain changes to your daily behaviour and routine can help reduce the itching and discomfort caused by the disease, and should:
- try to keep your skin moisturised at all times
- protect the skin from any damage
- in case of lesions in the mouth caused by the disease, take care of good oral hygiene and visit the dentist regularly
- It is also possible to reduce oral pain and other unpleasant sensations by giving up smoking, drinking alcohol and avoiding spicy, acidic foods and drinks


Nail psoriasis
Psoriasis is a form of chronic systemic inflammatory autoimmune disease that mostly affects fingernails and toenails.
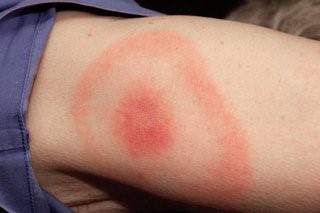
Lyme disease
It is contracted when a blood-sucking tick injects intestinal contents containing bacteria into a wound. Untreated Lyme disease can damage not only the skin, but also the internal organs, joints and nervous system.
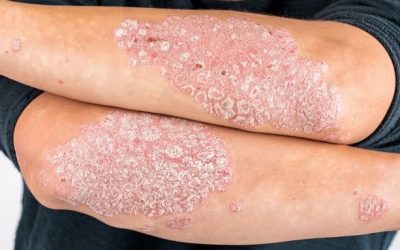
Psoriasis
A common, chronic, inflammatory, recurring skin disease that affects 2-3% of the population. Psoriasis can start at any age, and is most often found in adults.
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškės g. 99, Vilnius
+370 671 33323
info@iderma.lt