Chilblains (Pernio)
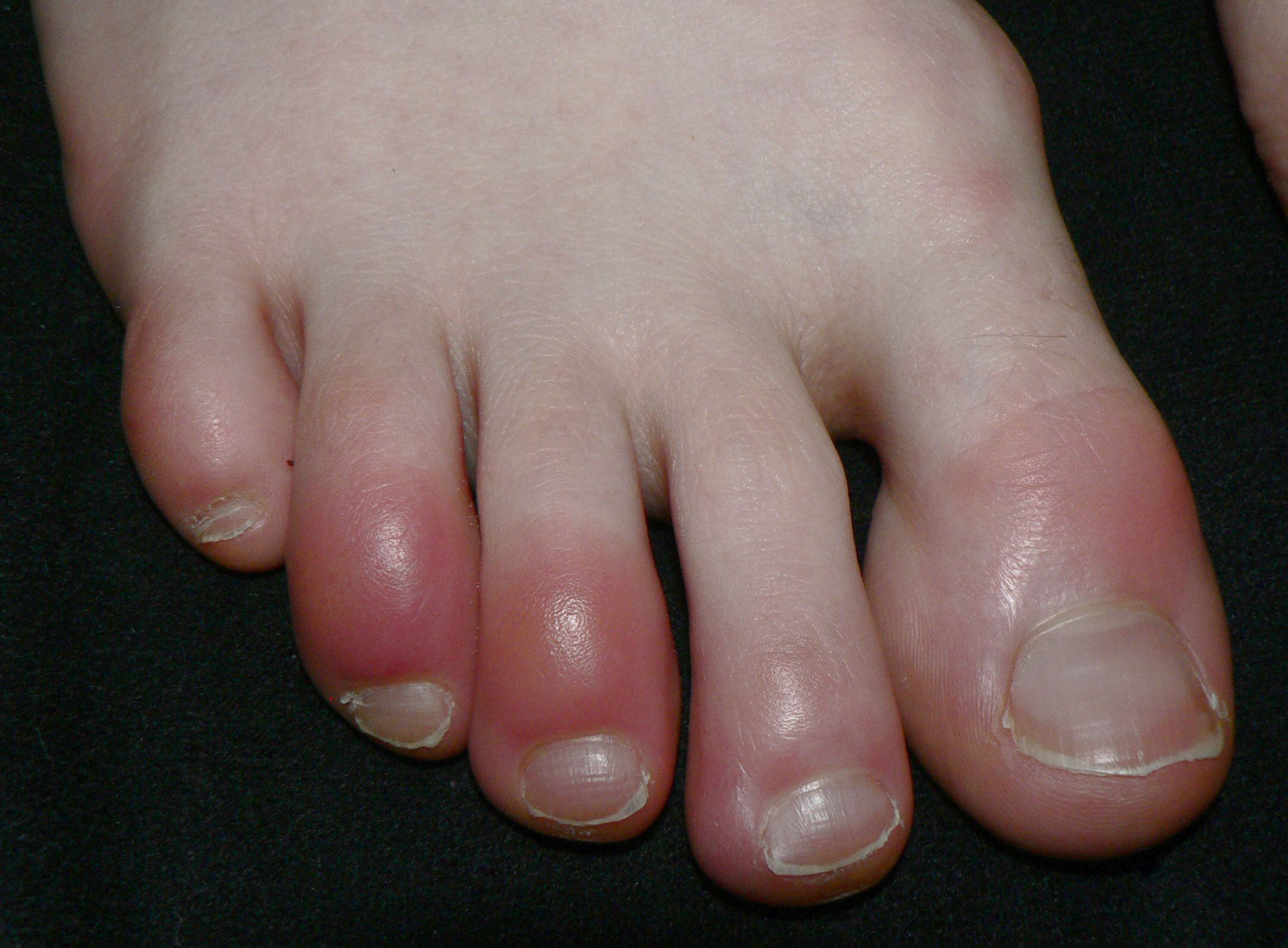
Chilblains (Pernio)
is a pathological skin condition characterised by reddening or bruising of the skin caused by exposure to low temperatures, high humidity and sudden changes in temperature. This is a common phenomenon, but why it occurs is not clear. Skin damage is thought to be caused by an abnormal vascular response to the cold that accompanies a sudden thaw, causes oxygen deprivation in tissues, stimulating an inflammatory response. In addition, small blood vessels can dilate faster than nearby larger ones when the skin warms up, increasing their permeability, allowing fluids to leak out of the blood vessel radius into the surrounding tissues and causing swelling.
Clinical signs
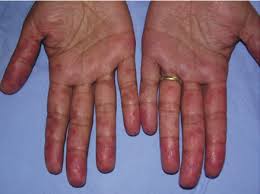
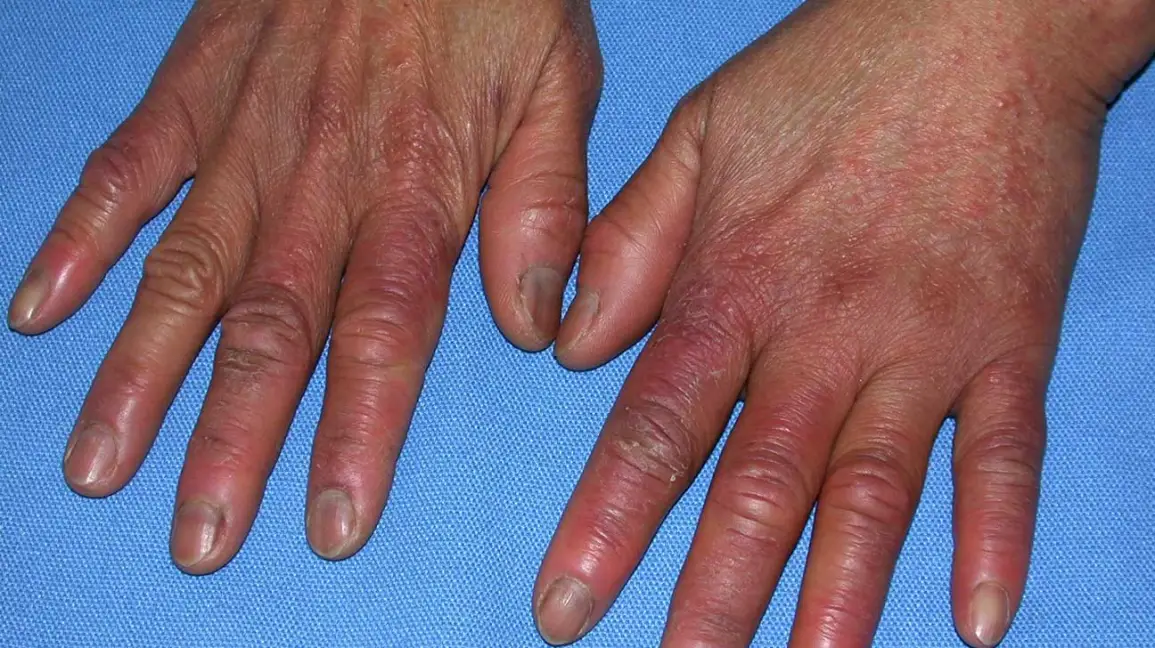
The dorsal surfaces of the hands or toes are the most commonly affected areas. Less often, scabs are observed on the nose, earlobes and front of the thighs – the areas most likely to cool.
The skin lesion is characterised by red or purple spots, plaques, papules, nodules in areas exposed to cold, accompanied by itching, pain, burning, swelling, blisters, ulcers, which may be complicated by secondary bacterial infection. Dry, flaky skin. In many patients, frostbite manifests as an acute lesion that starts 12-24 hours after frostbite.
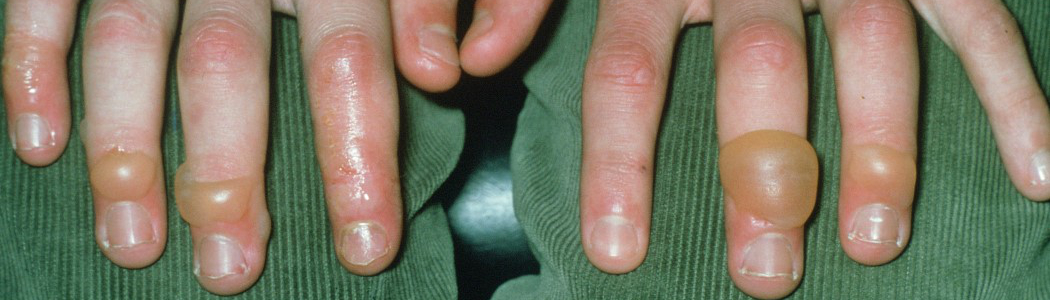
The following factors increase the risk of pressure sores: lower than normal body weight, increased sweating, female gender (pressure sores are most common in young or middle-aged women), impaired circulation due to comorbidities (increased sensitivity to changes in temperature), time of the year and weather conditions (high humidity and cool air), smoking (vascular diseases, impaired wound healing), and family history. Frostbite is also more common when the hormonal background of the body changes, which is why frostbite is more frequent during pregnancy. The provoking factor may be a minor trauma in an area not exposed to the cold.
Treatment and prevention:
Recurrence can be observed every year at the start of the cold season. It is important to thaw the affected areas gradually, as a sudden thawing of the frozen skin can worsen the condition. Do not massage, rub, apply direct heat… When it gets cold, it is better to drink tea or other hot beverages to warm the whole body. Avoid exposure to cold as much as possible. It is important to keep the affected skin warm and dry, but away from direct heat sources (wear gloves, socks). Baths no warmer than 10 degrees and lasting 15-30 minutes are possible. Application of a lotion or cream to nourish the skin to relieve itching is also possible. In the case of erosions and ulcerations, it is important to disinfect with antiseptics and, if necessary, gently scrub to prevent infection. It is important to avoid biting. Secondary bacterial infection is a possible and common complication of skin damage.
A doctor’s consultation is needed in case of complications – unusually severe pain, skin sensitivity, suspected infection, or if the skin condition does not improve within one or two weeks. If the symptoms continue to bother you during the warmer months and become chronic and recurrent, it may be advisable to consult a doctor to investigate other possible diseases.
It is important to avoid or limit outdoor exposure in cold and wet weather. It is advisable to wear several layers of loose clothing, mittens, cotton-lined, waterproof gloves, wool socks, warm and waterproof footwear – it is important to cover as much exposed skin as possible. Keep hands, feet and face dry and warm. Use nutritious, oily creams, ointments containing little or no water 30 minutes before being outdoors on areas of the face, body not protected from the cold. It is recommended to reduce the use of such as caffeine, decongestants. When it gets cold, do not try to thaw the extremities quickly, exercise (physical activity promotes blood circulation), stop smoking.
Forecast:
Although scaling is an unpleasant skin lesion, the prognosis for this pathology is good, and it usually does not lead to serious consequences. Symptoms usually resolve spontaneously, without any adverse reactions, within 1-2 weeks if cold and infectious complications are avoided.

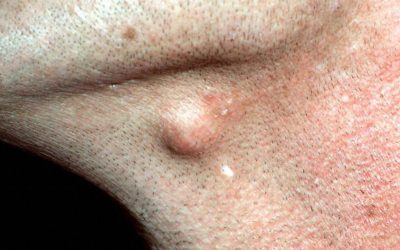
Epidermoid cysts
Benign skin formation (cyst) formed at the place of hair growth, inside is usually filled with keratin and fatty filler.
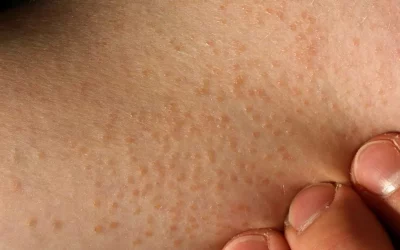
Lichen nitidus
A rare inflammatory skin disease characterized by small, flesh-colored, shiny bumps on the skin.
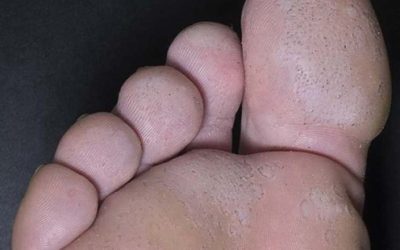
Pitted Keratolysis
Non-inflammatory, bacterial skin disease of the palms and soles. Dotted pits are visible in the damaged skin, and an unpleasant smell is felt.
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškės g. 99, Vilnius
+370 670 70 822
info@iderma.lt