Vasculitis
Vasculitis – inflammation of blood vessel walls, which can cause damage to internal organs and skin.
- A rare disease classified according to the size of the affected blood vessels:
-
- Large blood vessels (more often affects large arteries: the aorta and its largest branches)
- Medium-sized blood vessels (coronary, intestinal, renal arteries are more often affected)
- Small blood vessels
-
- Often the cause remains unknown
- Risk factors that can promote the development of the disease:
- infections (hepatitis B, C)
- blood cancer
- immune system diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma)
- drug reactions
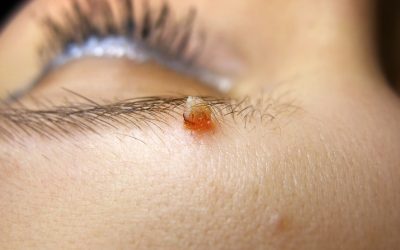
Petechiae

Ulcers
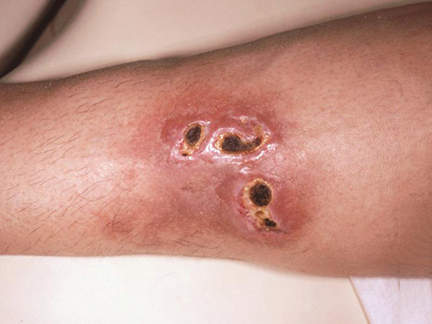
Blood blister
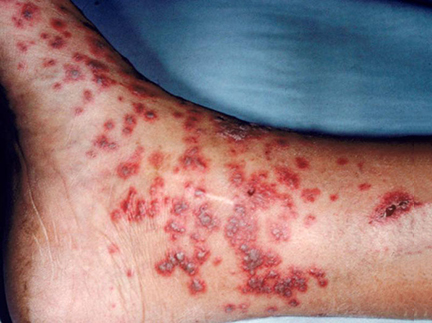
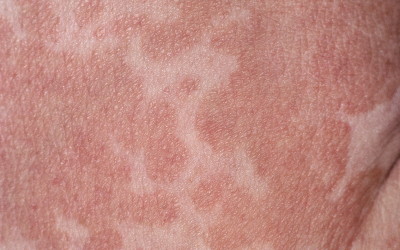
livedo reticularis
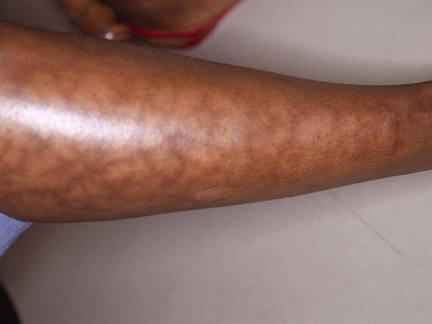
Reddish nodules
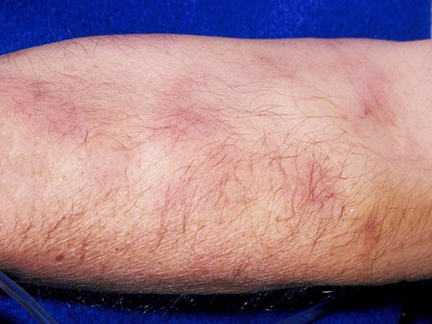
Clinical symptoms
Common symptoms of vasculitis may include:
- fever
- headache
- tired
- weight loss
- full body aches and pains
In rarer cases it may affect:
- digestive system
- eyes
- ears
- lungs
- skin
Vasculitis can occur only in the skin, or the symptoms appearing in the skin can be a partial expression of a systemic disease affecting other organs.
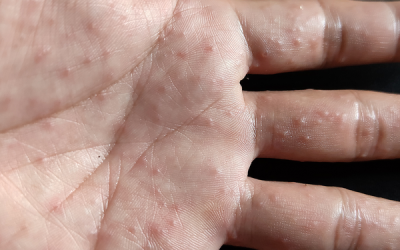
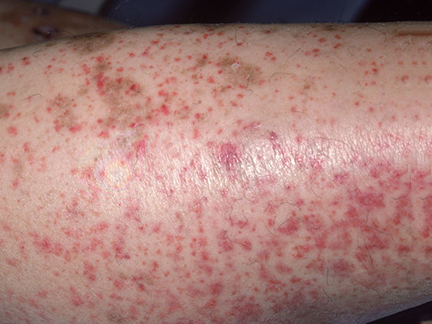
A skin lesion is characterized by:
- red dots (petechiae)
- reddened nodules
- ulcers
- blisters filled with blood
- blisters (red, more burning, painful than itchy skin bumps)
- livedo reticularis (localized or widespread, spotted network of blood vessels with a red-blue or pink tint)
Diagnostics
In the presence of changes only in the skin, a detailed survey and examination of the patient is usually sufficient to establish the diagnosis of vasculitis. In rare cases, a skin biopsy is performed. However, in order to determine the cause of the disease or to confirm systemic vasculitis, detailed studies are required, during which other diseases with similar manifestations are excluded. Such studies can be:
- laboratory tests (inflammatory markers, autoantibodies in the blood)
- imaging studies
- angiography
- biopsy of the skin or affected organs
Treatment
During the consultation, the treatment is selected for each patient individually. The goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation and symptoms caused by the disease. If vasculitis occurs only in the skin, the prognosis is usually good, the symptoms may go away on their own. If there is damage to other organs, systemic immunosuppressive drugs are usually required.

Soft fibromas (papillomas)
Soft fibromas (papillomas) Soft fibroids (papillomas) are benign, non-infectious, non-contagious skin lesions that are harmless...
Multi-coloured ringworm
Multi-coloured ringworm Multi-coloured ringworm is a skin rash caused by a fungus of the Malassezia species, called...
Dishidrotic eczema
Dishidrotic eczema Dishidrotic eczema (syn. dishidrotic dermatitis, dishidrotic dermatitis, pompholyx) is a chronic,...
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškių g. 99, Vilnius
+370 670 70822
info@iderma.lt