Mycosis Fungoides
- the disease occurs twice as often in men than in women
- more typical in older age (between 55-60 years)
- 15 – 17 percent more common in North America and Asia than in Europe
accounts for 39% of all skin lymphomas
Risk factors
Although the exact causes of the disease have not been clarified, certain factors can lead to the appearance of the disease:
- UV rays
- infections (Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, HIV)
- various occupational factors (irradiation, chemicals)
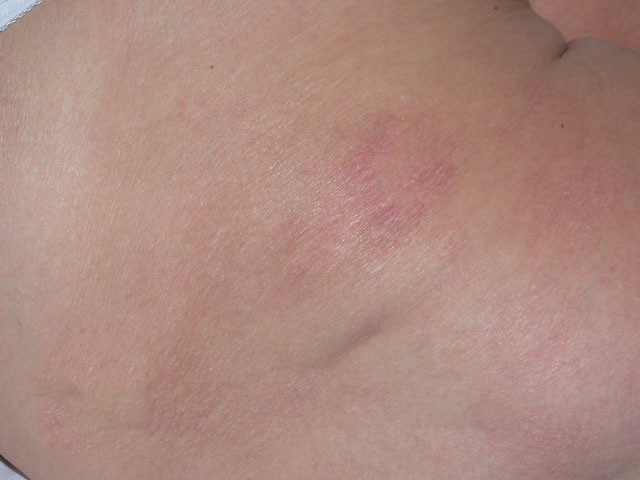

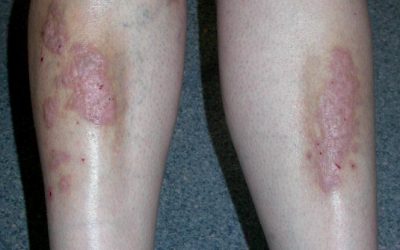
Plaque phase
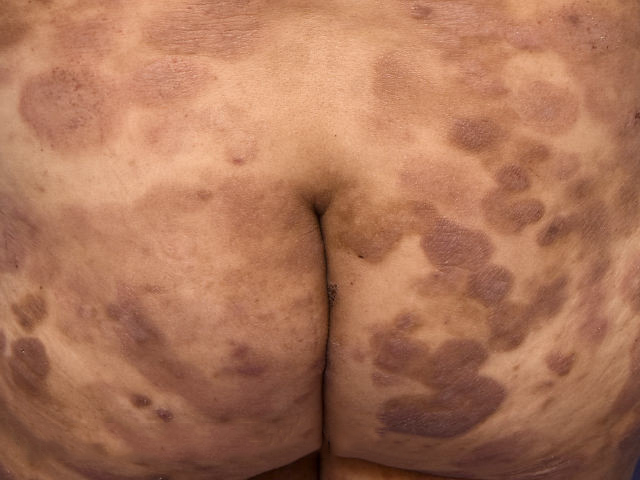
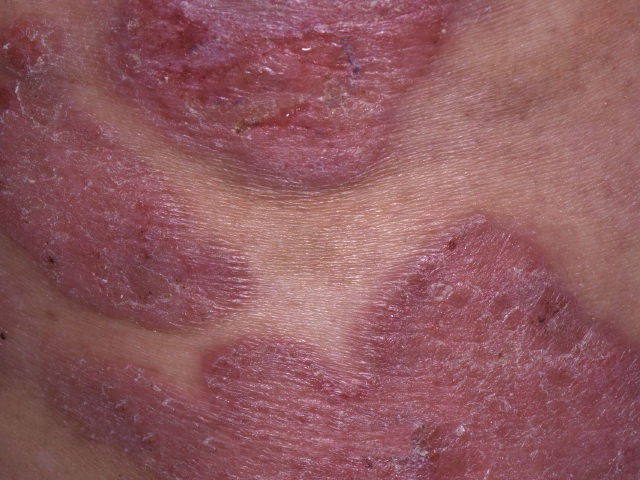
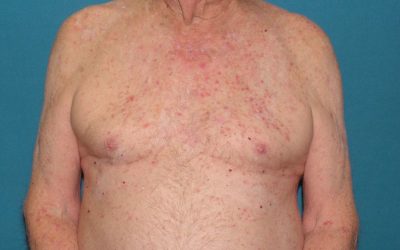
Tumor phase
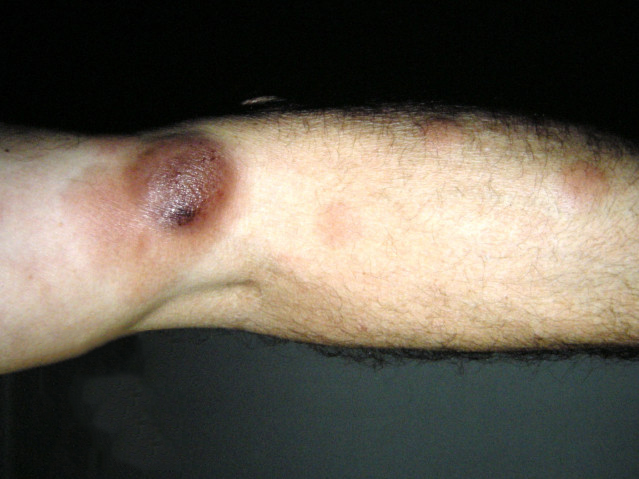
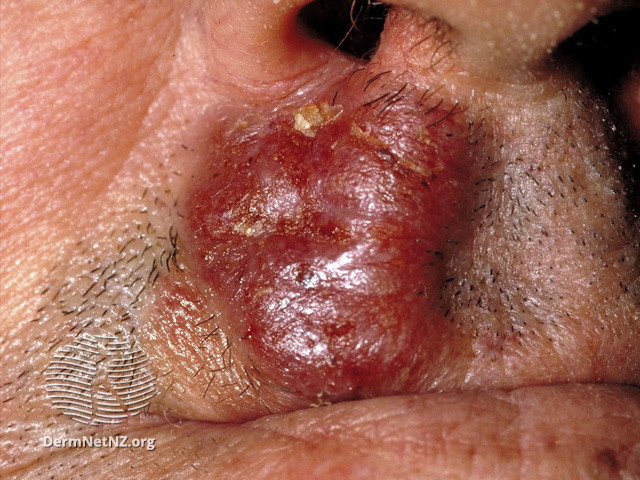
Mycosis Fungoides is characterized by three main stages, several of which may exist at the same time:
- Patch phase – characterized by pink, scaly spots of various sizes, which can be localized or spread in areas of the skin that do not receive sunlight. Usually an early sign of the disease.
- Plaque phase – pinkish or brownish color, larger skin bump, with irregular edges and different involvement of the superficial skin layer.
- Tumor phase – a characteristic formation from 1 cm in size, may have arisen from the spot or plaque stage or formed immediately anew. Has a tendency to ulcerate. Growth rates vary greatly.
Diagnostics
In the early stages, diagnosis is complicated. Later, the patient’s survey and examination data, combining them with the response of the skin biopsy, are usually sufficient to diagnose the disease. Radiological examination methods are used to determine the spread of the disease.
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment and prognosis vary depending on the individual’s condition and the progression stage of their illness.
For early stages, the dermatologist might recommend localized treatments, light-based therapies, and low-intensity therapies.
In more advanced stages or for patients who do not respond to initial treatments, the plan may include medications that modify immune system responses, more intensive therapies, and advanced biological treatments.
For those in later stages, a form of cellular transplantation might be considered as a potential curative approach.

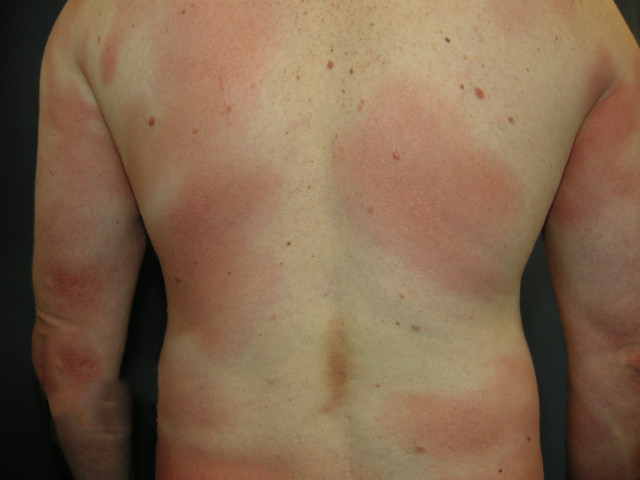
Lichen planus
Chronic, itchy skin disease manifested by well-defined, erythematous (red) spots, scales in mechanically damaged areas.
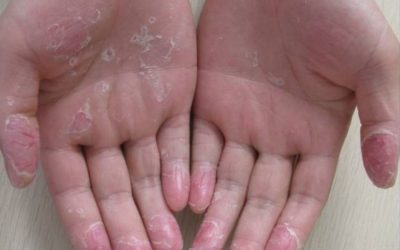
Keratolysis exfoliativa- one of the possible causes of skin peeling
A common skin condition that manifests as local peeling of the skin on the palms of the hands, less often on the soles of the feet.
Heat rash
A self-limiting, temporary skin condition caused by blockage of the eccrine (sweat) glands. There are 3 main types of rashes.