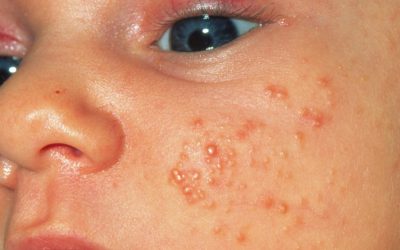
Lichen nitidus
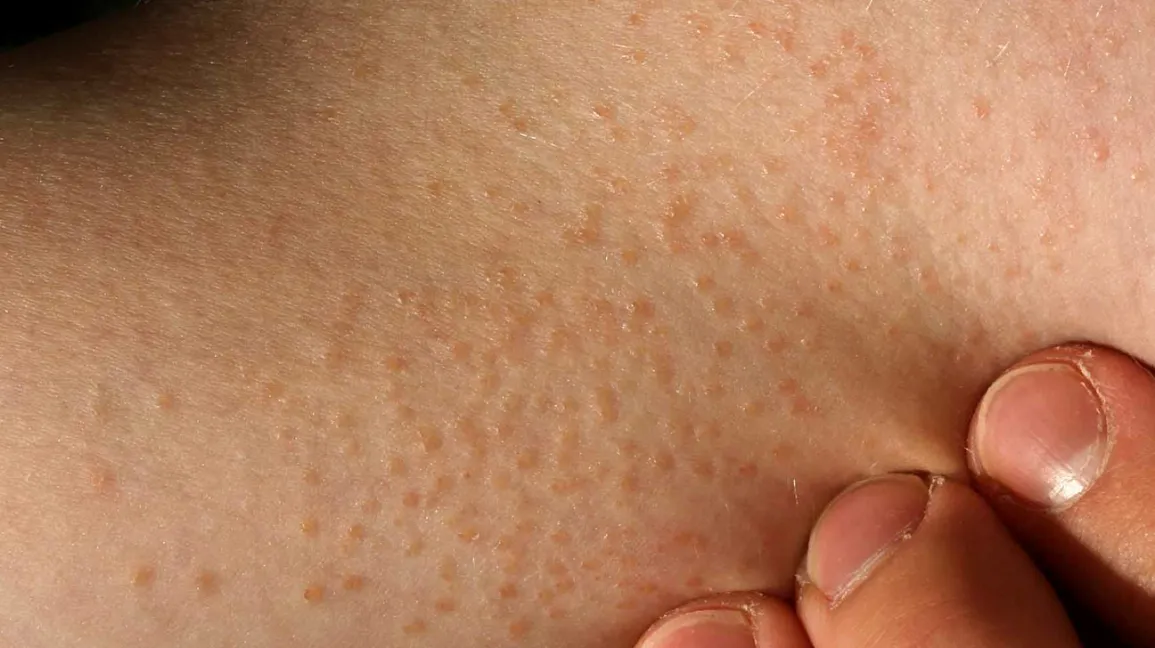
- It occurs equally often in both men and women
- More common in children and young adults
- The exact cause of the disease is not clear
- The manifestation of the disease may be related to genetics
- Characteristic to people with other diseases (lichen planus, atopic dermatitis, Crohn’s disease, tuberculosis and others)
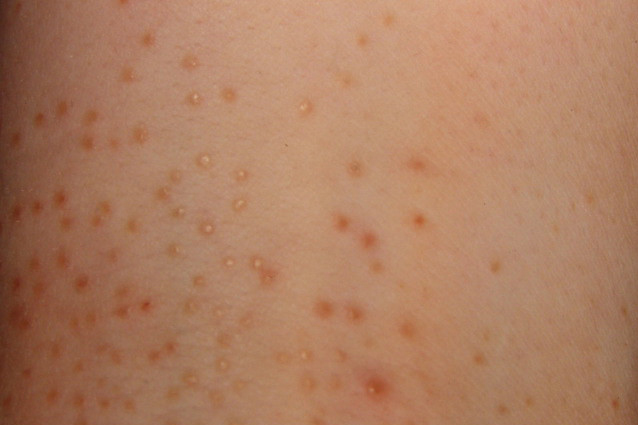
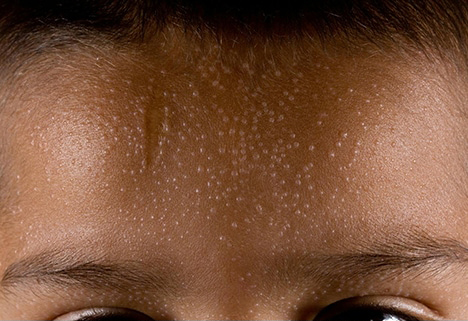
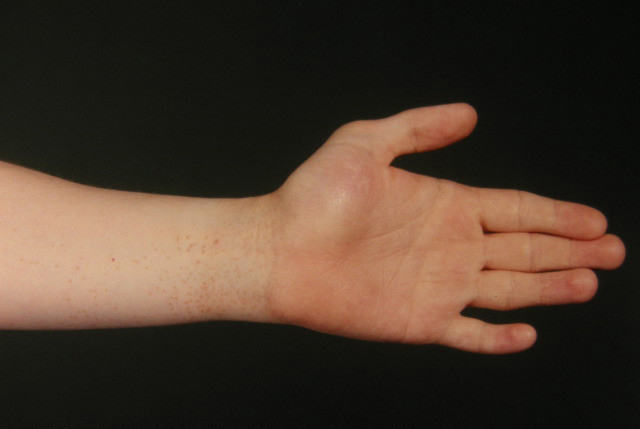
Clinical signs
Lichen nitidus is characterized by:
- Clusters of skin bumps (papules) of various sizes
- Papules are skin-colored, can vary from pink to dark brown, shiny, round, flat-topped
- In rare cases, they also appear in the mucous membranes, then the papules are flat and gray in color
- Sometimes nails are affected if the patient has a widespread form of the disease
- Localization: chest, abdomen, arms, genital area. It can migrate, disappearing in one place of the body, appearing in another
- In rare cases, itching may occur
The patient’s survey and examination data are usually sufficient to establish the diagnosis. In rare cases, a skin biopsy may be taken.
Treatment and prognosis
Lichen nitidus usually lasts from a few months to a few years. Often, the disease goes away on its own, and the skin remains unchanged. However, in the presence of itching or other bothersome symptoms, specific symptomatic treatment may be used. During the consultation, the treatment is selected for each patient individually.
For treatment can be used:
- hormone ointments
- topical retinoids
- other topical medications
- antihistamines
- phototherapy

Skin conditions in newborns
It is in the early period of the newborn that various adaptive changes in the skin of the newborn are observed, manifested as it adapts to new environmental conditions.
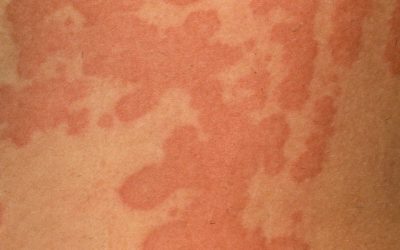
Acute urticaria
an acute vascular skin reaction that manifests as swelling of the skin, raised red blisters that are very itchy.
Geographic tongue
A benign inflammatory disease of the mouth characterized by the loss of cells of the surface layer of the tongue in its dorsal part.
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškių g. 99, Vilnius
+370 670 70822
info@iderma.lt