Chickenpox
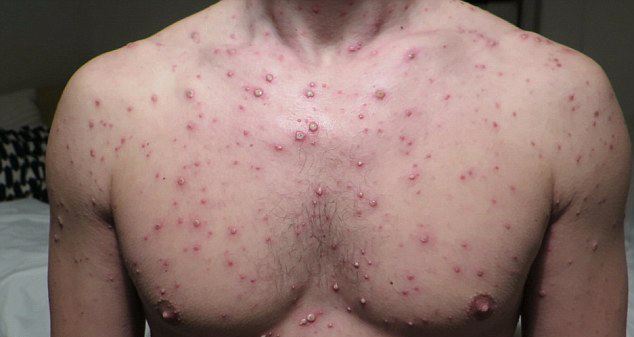
Chickenpox (lot. varicella) –acute viral disease manifested by fever, herpetic rash on the skin and mucous membranes.
- Causative agent: Varicella zoster virus belonging to the Herpesviridae family
- Children of preschool age are most often affected (mild form), adults and people with a weak immune system are characterized by a more severe form of the disease and a higher risk of developing complications
- The virus remains in the body for life, so when the immune system is weakened, it can cause another disease – shingles
- It is transmitted from a person with chickenpox: by direct contact or by airborne droplets. If a pregnant woman is sick, the fetus can become infected through the placenta. The virus dies quickly outdoors, so it is only contagious indoors
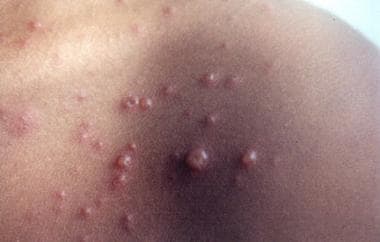
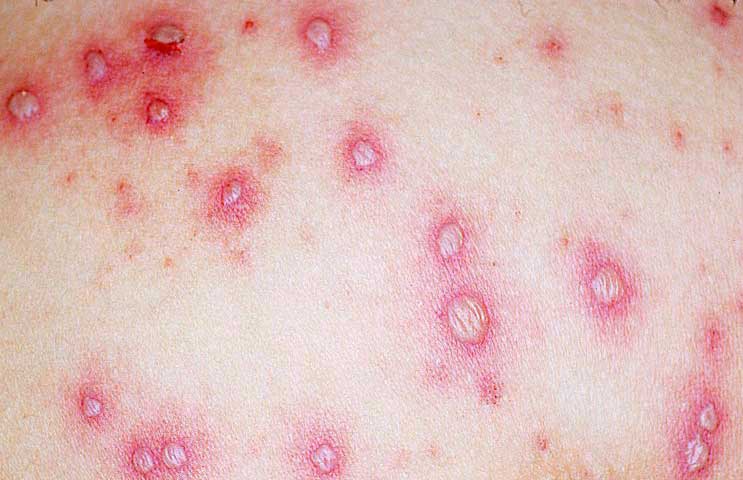
- The first symptoms of the disease appear 2-3 weeks after infection
- At the beginning of the disease, non-specific symptoms appear – fever, weakness, malaise
- Then the spots start to appear, which turn into blisters filled with a clear liquid.
- Scabs form as the rash fades. It breaks out in waves every 1-2 days, so you can see the elements of all stages of the rash in one area
- The rash is very itchy
- Localization of rashes: in the hairy part of the head, on the face, torso, limbs, mucous membrane (mouth, eyes, genitals)
- If you get sick during pregnancy, harm to the baby, miscarriages are possible
- After getting chickenpox, long-term immunity is formed, so it is rare to get sick again
Diagnostics
During the consultation, the patient’s interview and examination data are usually sufficient to determine the diagnosis. When interviewing the patient, it is important for the doctor to find out whether there was contact with a sick person. In rare cases, when data are missing, blood tests and a smear from the rash can be done.
Treatment
Since chicken pox is a highly contagious disease, the patient must be isolated for 10 days from the onset of the disease (it is mandatory not to let the child go to kindergarten, school, or take them outside).
Treatment is selected individually for each patient. The most important thing is hygiene, lying down, restoring fluid balance. Antiviral drugs may be prescribed in certain cases. Do not scratch the rash under any circumstances. If you suffer from severe itching, antihistamines may be prescribed.
Prevention
The best preventive measure for both children and adults who have not had chickenpox before is vaccinations.
It is very important to vaccinate adults who have not previously had chicken pox, but who have close contact or a high risk of contact with sick persons, as well as vaccination is required for persons whose immune system is weakened (those with HIV/AIDS, chronic diseases, malignant tumors, those using steroid hormones, drugs that suppress the immune system).
Important: Chickenpox vaccine should not be given to pregnant women. Vaccination is also not recommended for persons who have recently received a blood transfusion or received immunoglobulins.

Soft fibromas (papillomas)
Soft fibromas (papillomas) Soft fibroids (papillomas) are benign, non-infectious, non-contagious skin lesions that are harmless...
Multi-coloured ringworm
Multi-coloured ringworm Multi-coloured ringworm is a skin rash caused by a fungus of the Malassezia species, called...
Dishidrotic eczema
Dishidrotic eczema Dishidrotic eczema (syn. dishidrotic dermatitis, dishidrotic dermatitis, pompholyx) is a chronic,...
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškių g. 99, Vilnius
+370 670 70822
info@iderma.lt