Foot fungus -Athlete’s foot
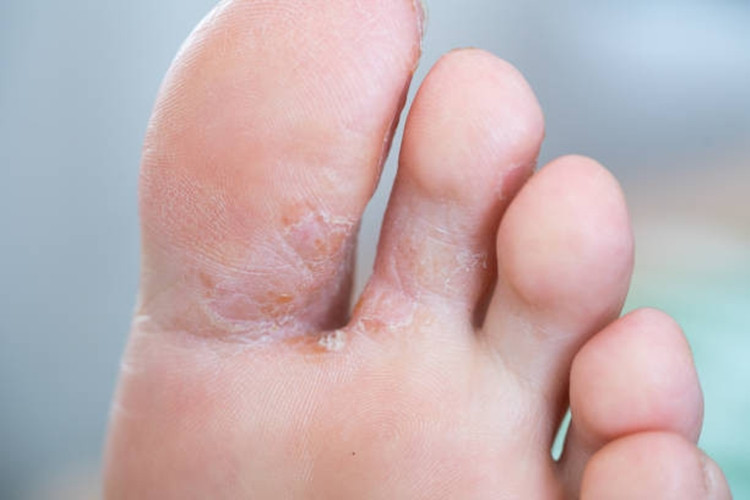
- The lifetime risk of developing athlete’s foot is 25%.
- A chronic course is characteristic, usually bilateral
- The most common causative agents: T. rubrum, T. interdigitale
- Source of infection: shoes, socks, carpets, public pools, gyms, saunas, showers, hotels
Risk factors
- fungal skin diseases in the family
- foot deformities
- visiting public pools
- injuries
- sensory disturbances in the feet
- Diabetes
- circulatory disorders in the legs
Classification
- Between the fingers
- Soles
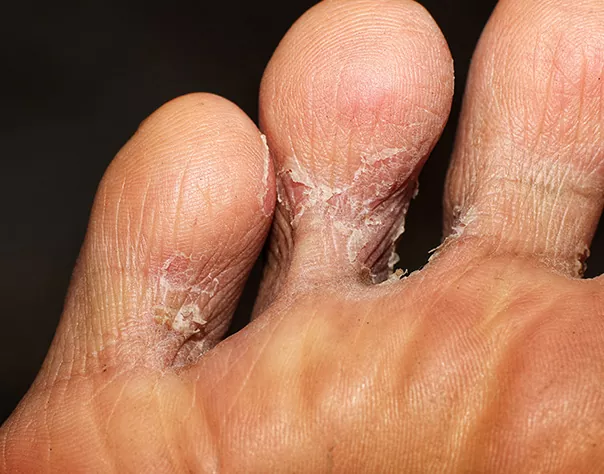
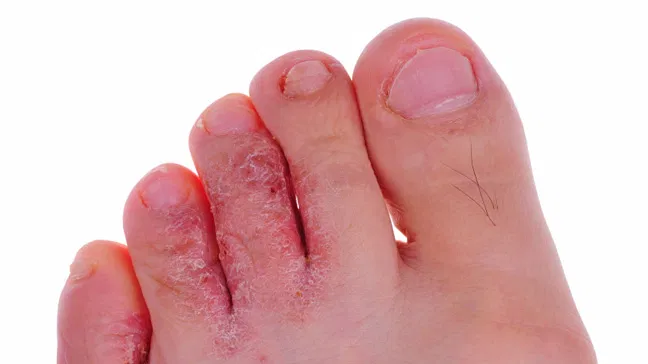
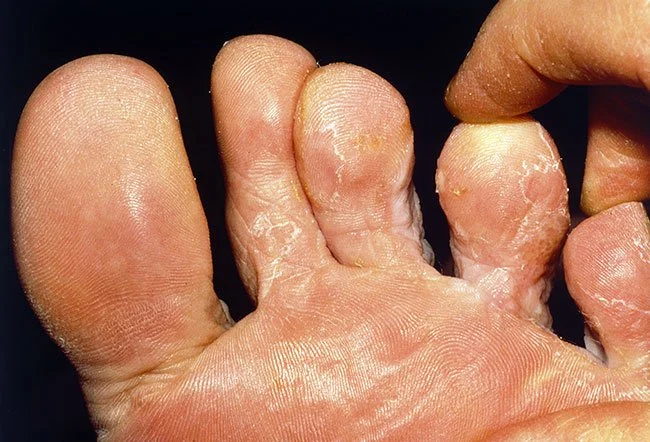
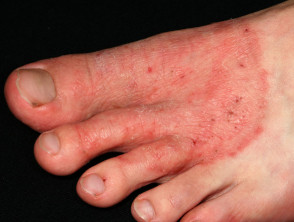
The appearance and symptoms of foot fungus depend on the form of the disease.
Between the fingers:
- characterized by flaking, redness, cracks, peeling of the stratum corneum (skin peeling) between the toes
Fungus of the soles occurs in two forms:
- one is more characterized by flaking, cracks, hardening of the skin
- may spread to the lateral and/or dorsal surface of the foot
- the other is more characterized by blisters in the arch of the foot that spread to the lateral surfaces. When the blisters burst, small defects of the surface layer of the skin (erosions) and scabs are formed
- itching is also characteristic
Diagnostics
In most cases, it is enough to make a diagnosis:
- anamnesis
- clinical signs
In rare cases, when the data from the anamnesis and the clinic are insufficient, laboratory tests are performed:
- dandruff microscopy. The test shows whether the fungus and its parts (hyphae, spores) are found in the sample
- microbiological test identifies the exact type of causative agent and determines the sensitivity to antifungal drugs
During the consultation, the treatment is selected for each patient individually. Topical antifungal drugs are the first choice treatment. Systemic oral antifungal drugs are prescribed if:
- widespread form of fungus
- a form resistant to local treatment
Prevention
- do not walk barefoot in swimming pools, hotels, gyms
- use separate hygiene products
- use disinfectants
- avoid humid working environment

Vitiligo – Why Do White Patches Appear on the Skin and How to Treat Them?
Vitiligo is a non-contagious skin condition characterized by white patches due to the loss of pigment. While it does not pose a direct threat to physical health, it can have a significant psychological impact. Learn what causes vitiligo, its symptoms, how it is diagnosed, and which treatment methods are currently available.
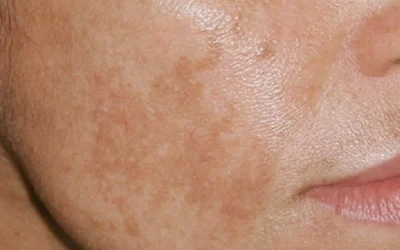
Hyperpigmentation: Causes, Types, and Modern Treatment Options
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by dark spots that appear due to sun exposure, hormonal changes, or skin damage. In this article, you will learn about the main types and causes of hyperpigmentation, as well as how to effectively treat it using modern dermatological methods and preventive care.
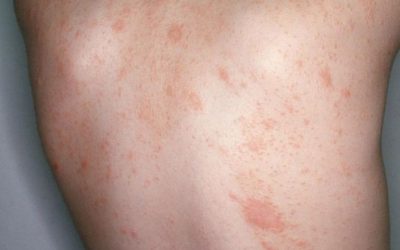
Pityriasis rosea
An acute, self-limiting, exanthematic skin disease that manifests as itchy, somewhat inflammatory, scaly rashes, usually on the torso, chest, and upper limbs.
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškių g. 99, Vilnius
+370 671 33323
info@iderma.lt