Scabies
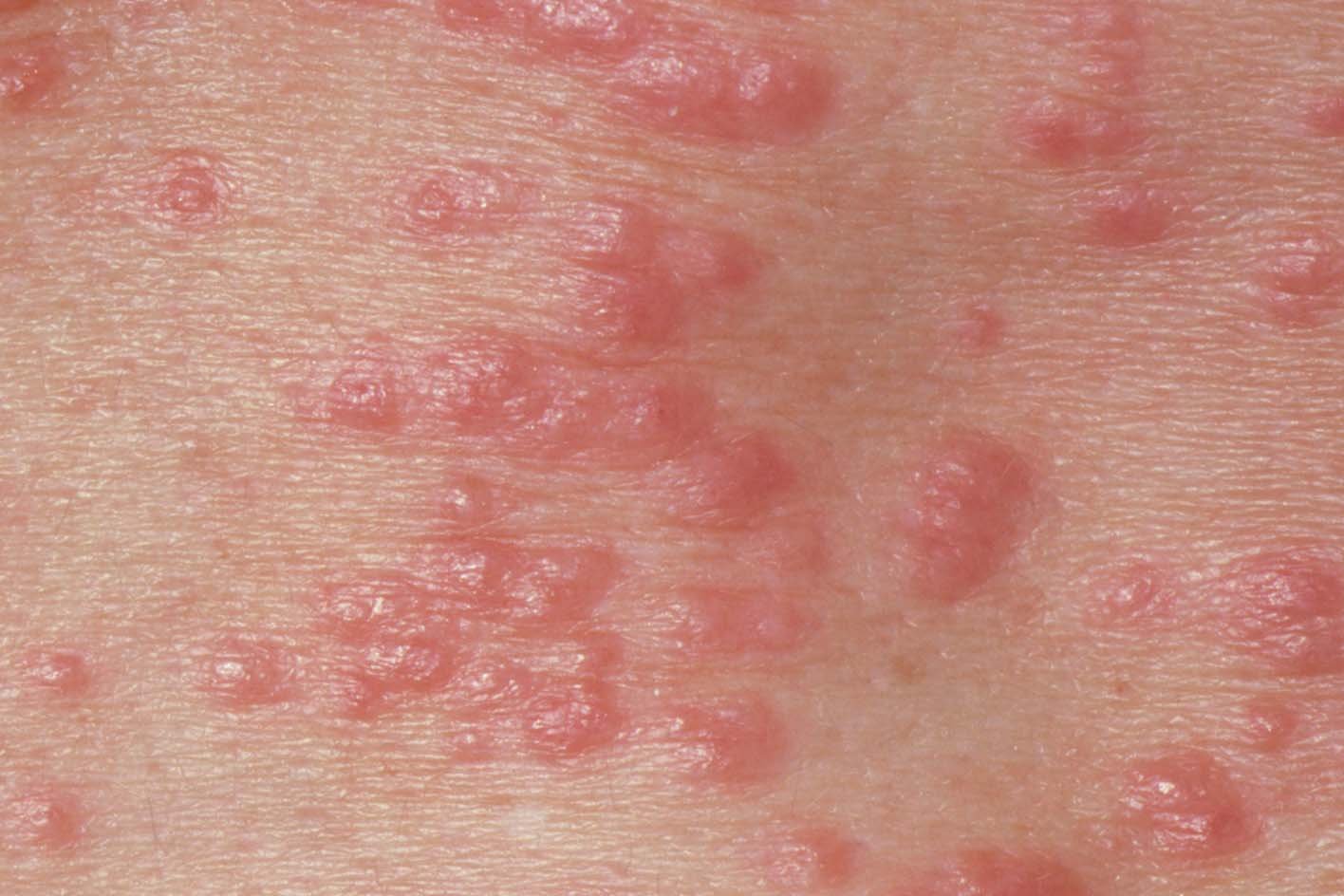
Scabies – A contagious parasitic skin disease characterized by extreme itching.
- Caused by: Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis (mites)
- Mites mate on the surface of the skin, males die quickly
- Without a host (human), ticks survive in the environment for 3-4 days.
- Spread by direct contact with a sick person or through infected objects
- The disease manifests itself in 1-8 weeks from the day of infection
Risk factors:
- poor diet
- weakened immune system
- bad hygiene
- old age
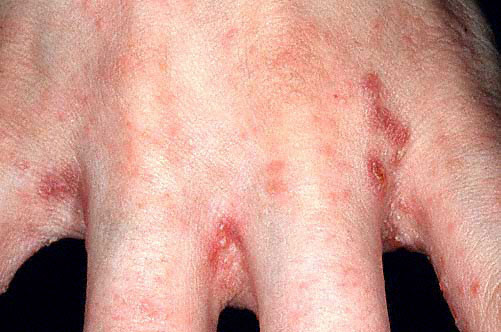
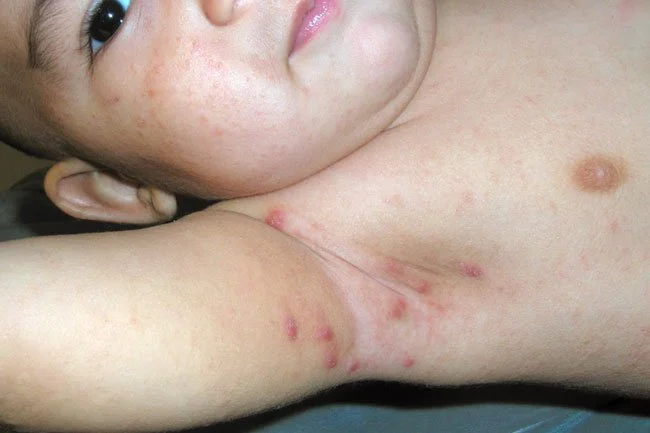
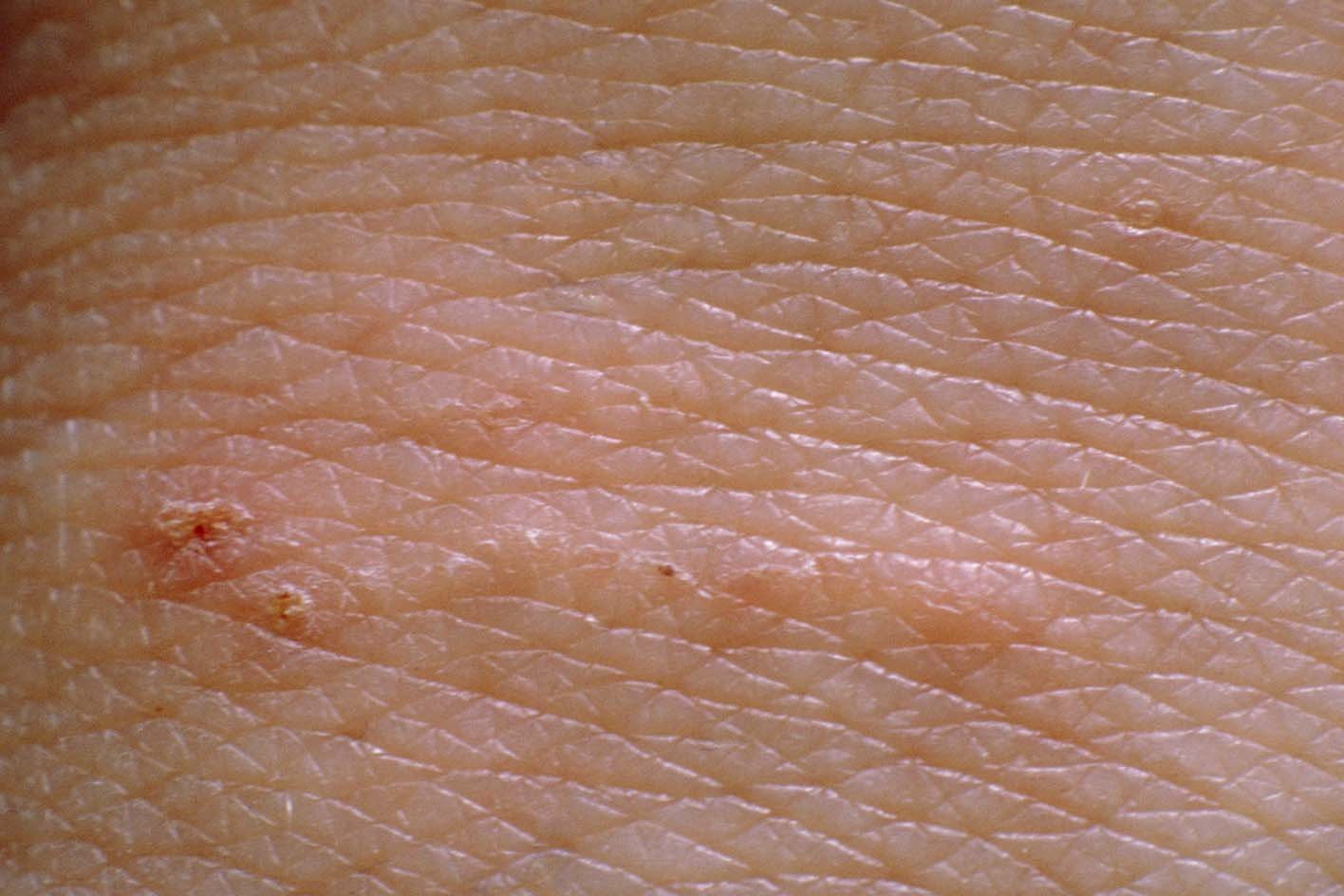
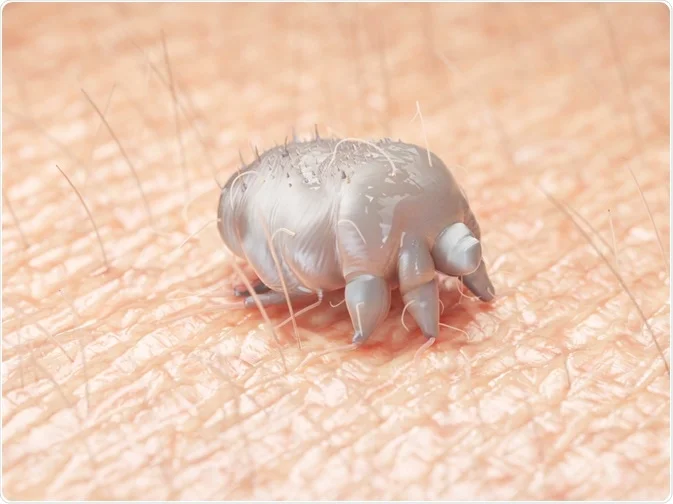
Clinical Signs
- Characterized by severe skin itching (especially at night), which may persist even for several weeks after the end of treatment
- Rashes:
-
- characteristic at the beginning of the disease elongated paired scaly papules (palpable bumps on the skin), also known as tick tracks
- localization of rashes: interfingers, palms, wrists, elbows, nipples, navel
- after 2 weeks from the onset of symptoms, as a hypersensitivity reaction of the body, generalized rashes (spread over most of the body) may occur
- then the face and scalp are usually not affected
- characteristic erythematous (reddish) papules on the skin of the trunk and limbs
- sometimes diffuse nummular (coin) dermatitis may occur, which is characterized by coin-shaped, very itchy rashes with plaques (larger than papules, palpable bumps on the skin)
- blisters on the palms and soles are also common
- papules, nodules in the groin, genital area
-
Diagnostics
It is usually enough to establish a diagnosis:
- anamnesis
- clinical signs
If there are insufficient data from the anamnesis and the clinic, then the following can be performed:
- dermatoscopy
- microscopy
Treatment
During the consultation, an individual treatment is selected for each patient, the aim of which is to eradicate the parasites that cause the above-mentioned symptoms. Ointments for the skin of the whole body (permethrin, benzoyl benzoate) or systemic treatment with oral drugs can be chosen for treatment.
Prevention and disinfection
Prevention:
- the patient must avoid contact with people for 24 hours after using medication
- all patients of the same focus should be treated simultaneously
- screening of family members, team, workplace and sexual partners is required
- the patient must use personal hygiene measures, sleep separately from other family members
Disinfection:
- patient’s clothes and bedding, used for 4 days before treatment must be washed in >60º C water or boiled in 1-2%. in a soda solution or with detergents for at least 10 minutes.
- clothes that cannot be washed are ironed on both sides with steam or placed in plastic bags and stored for 4 days
- coats, fur and leather products are stored outside for 5 days (during the cold season, 1 day at sub-zero temperatures)

Vitiligo – Why Do White Patches Appear on the Skin and How to Treat Them?
Vitiligo is a non-contagious skin condition characterized by white patches due to the loss of pigment. While it does not pose a direct threat to physical health, it can have a significant psychological impact. Learn what causes vitiligo, its symptoms, how it is diagnosed, and which treatment methods are currently available.
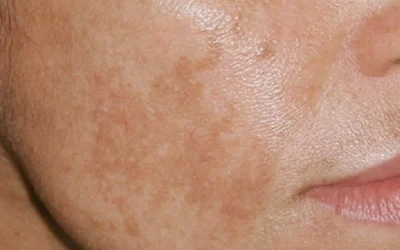
Hyperpigmentation: Causes, Types, and Modern Treatment Options
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by dark spots that appear due to sun exposure, hormonal changes, or skin damage. In this article, you will learn about the main types and causes of hyperpigmentation, as well as how to effectively treat it using modern dermatological methods and preventive care.
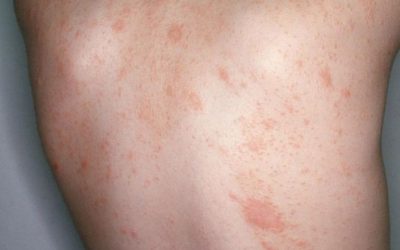
Pityriasis rosea
An acute, self-limiting, exanthematic skin disease that manifests as itchy, somewhat inflammatory, scaly rashes, usually on the torso, chest, and upper limbs.
iDerma
MB iDerma
Fabijoniškių g. 99, Vilnius
+370 671 33323
info@iderma.lt