Paraneoplastic dermatological manifestation of gastrointestinal malignancies
Possible skin lesions:
- Acanthosis nigricans
- Florid papillomatosis
- Necrolytic Migratory Erythema
- Palmoplantar keratoderma
- Pancreatic panniculitis
- Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis
- Pityriasis rotunda
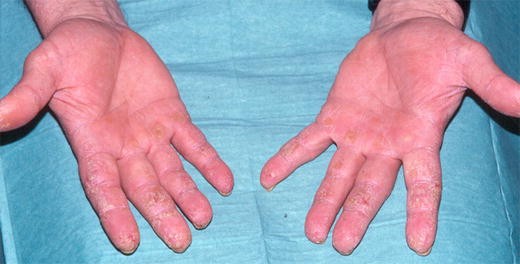
Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis (otherwise known as Bazex syndrome) – lesions similar to psoriasis or eczema are characteristic scaly patches of purple hue. Nail damage is also possible.
Localization:
- Hands, feet, knees, ears, nose and cheeks
- May be around the nails or damage to the nails themselves
Localization:
- Typically on bending surfaces
- Other places: back of the neck, armpits, groin
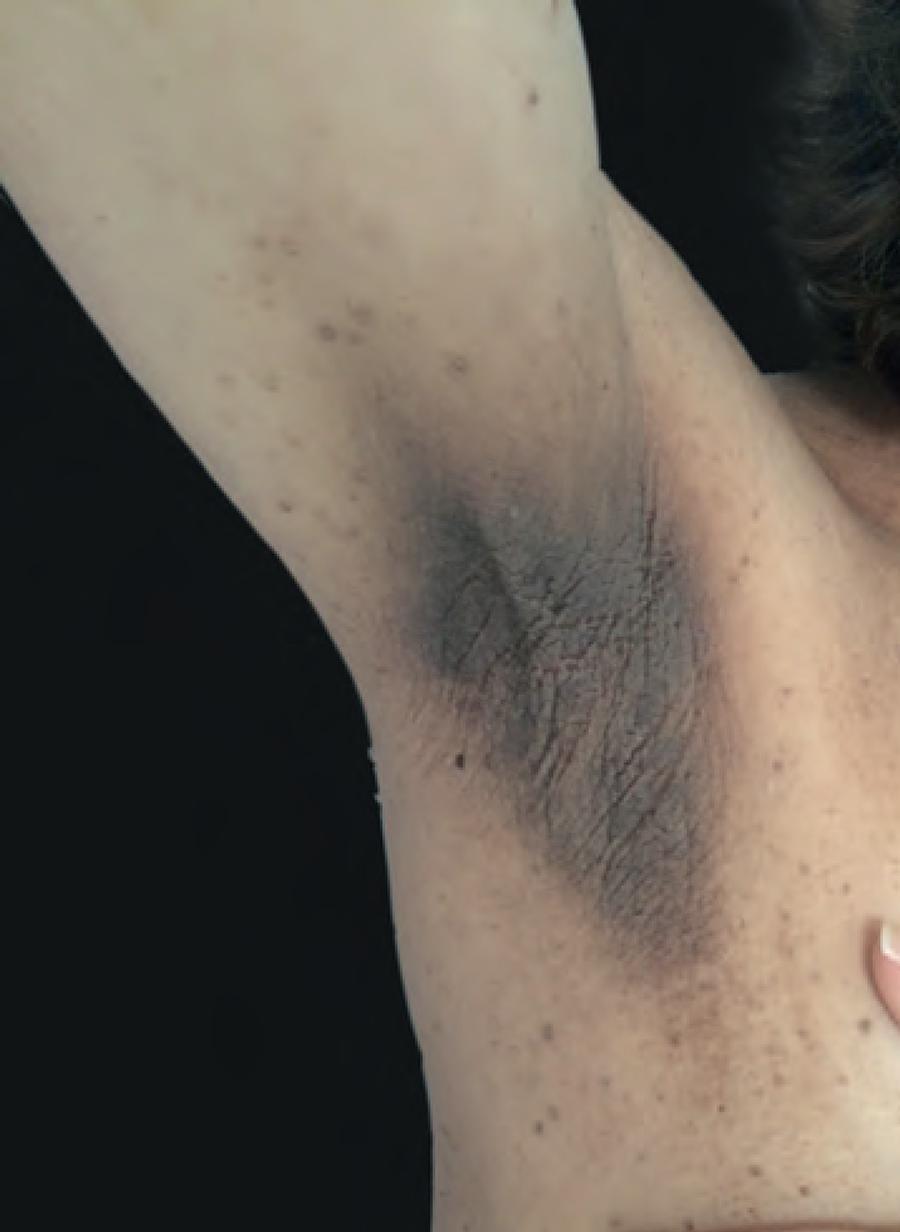
Localization:
- Body folds – in the torso, groin, buttocks, thighs
- May be around the mouth area
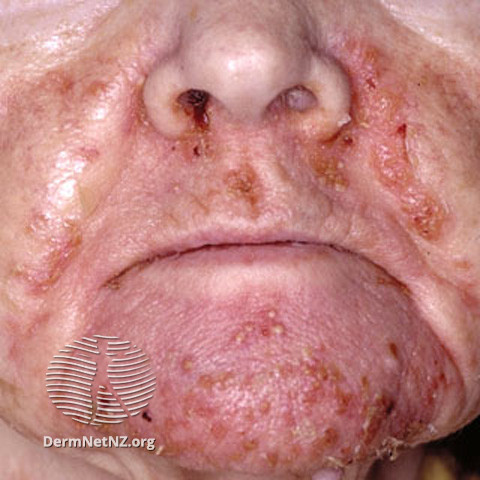
sudden onset is characterized by abundant papillomas (warts) resembling viral warts. Growths are small in size (1-3 mm in diameter), with time they spread to other areas of the body. Itching occurs in 50% of cases.
Localization:hands, feet, knees, ears, nose and cheeks.
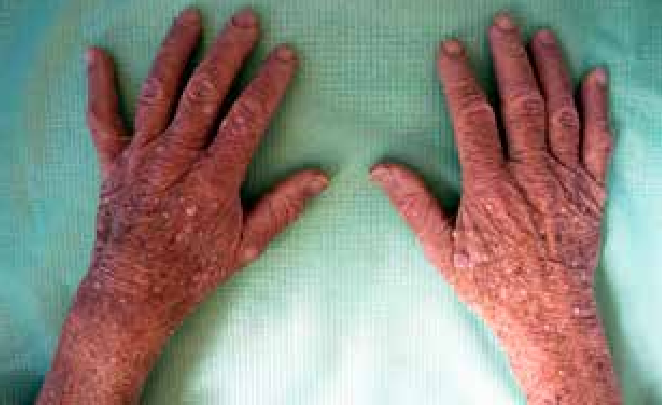
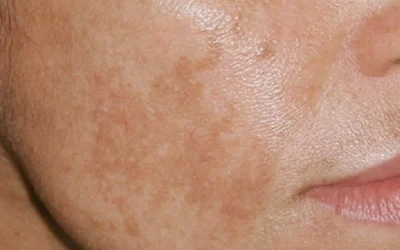
- Pink or light brown in color
- Hyperpigmented (darker than skin color) – if the skin is dark. Hypopigmented (lighter than skin color) – if the skin is light.
Localization: torso and limbs

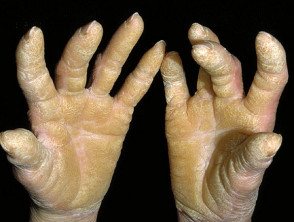
Localization: palms and soles
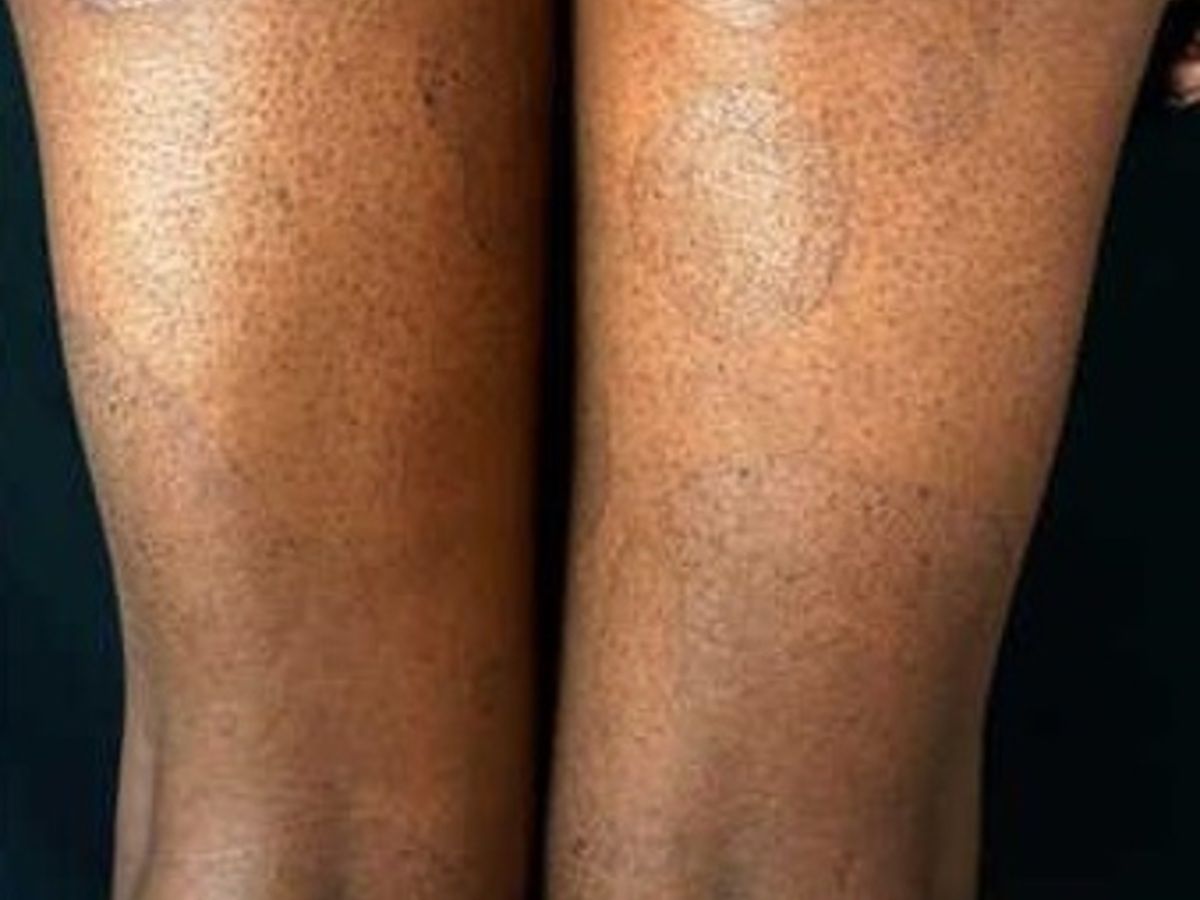
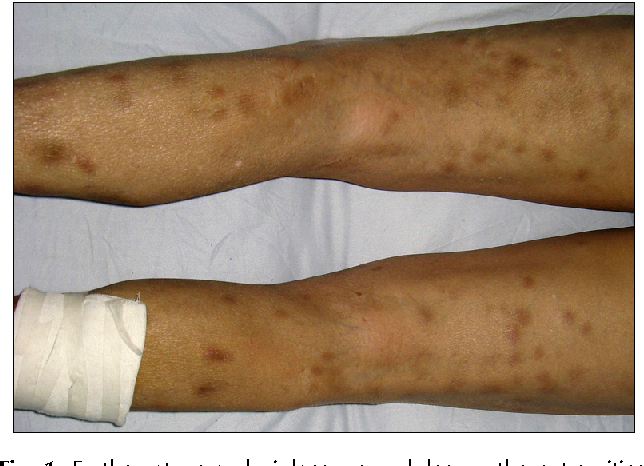
Localization: legs, torso, buttocks
Certain criteria are used to assess whether the skin disease is a paraneoplastic syndrome:
- Neoplasia and paraneoplasia begin at the same or similar time
- Parallel course of conditions (as the tumor mass decreases, skin damage also decreases or vice versa)
- Signs of a skin condition are not part of a genetic syndrome
- A certain malignancy is associated with a certain paraneoplastic skin disease
- A rare prevalence of skin disease in the general population
- A frequent association between neoplasia and paraneoplasia
Treatment
The dermatologist carefully devises a tailored treatment strategy for each patient, considering the unique aspects of the paraneoplastic syndrome and the associated cancer.
The primary approach involves addressing the underlying cause of the syndrome.
This could encompass a variety of general treatment methods. Additionally, managing the particular symptoms of the syndrome plays a crucial role in enhancing the patient’s overall well-being.

Vitiligo – Why Do White Patches Appear on the Skin and How to Treat Them?
Vitiligo is a non-contagious skin condition characterized by white patches due to the loss of pigment. While it does not pose a direct threat to physical health, it can have a significant psychological impact. Learn what causes vitiligo, its symptoms, how it is diagnosed, and which treatment methods are currently available.
Hyperpigmentation: Causes, Types, and Modern Treatment Options
Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by dark spots that appear due to sun exposure, hormonal changes, or skin damage. In this article, you will learn about the main types and causes of hyperpigmentation, as well as how to effectively treat it using modern dermatological methods and preventive care.
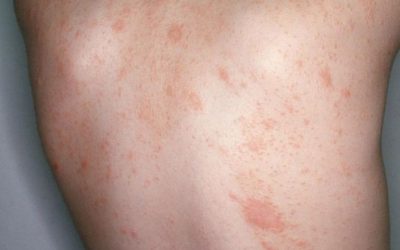
Pityriasis rosea
An acute, self-limiting, exanthematic skin disease that manifests as itchy, somewhat inflammatory, scaly rashes, usually on the torso, chest, and upper limbs.